So, when we speak of organization, we are not to think simply of the externals; of that which goes by the name “school system”—the school board, the superintendent7, and the building, the 78engaging and promotion of teachers, etc. These things enter in, but the fundamental organization is that of the school itself as a community of individuals, in its relations to other forms of social life. All waste is due to isolation9. Organization is nothing but getting things into connection with one another, so that they work easily, flexibly, and fully10. Therefore in speaking of this question of waste in education, I desire to call your attention to the isolation of the various parts of the school system, to the lack of unity8 in the aims of education, to the lack of coherence11 in its studies and methods.
I have made a chart (I) which, while I speak of the isolations of the school system itself, may perhaps appeal to the eye and save a little time in verbal explanations. A paradoxical friend of mine says there is nothing so obscure as an illustration, and it is quite possible that my attempt to illustrate12 my point will simply prove the truth of his statement.
The blocks represent the various elements in the school system, and are intended to indicate roughly the length of time given to each division, and also the overlapping13, both in time and subjects studied, of the individual parts of the system. With each block is given the historical conditions in which it arose and its ruling ideal.
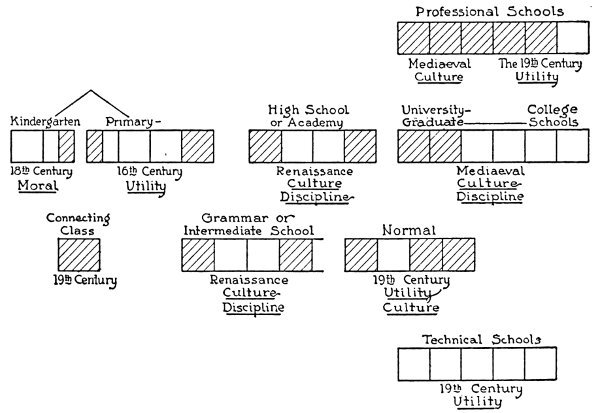
The school system, upon the whole, has grown from the top down. During the middle ages it was essentially14 a cluster of professional schools—especially law and theology. Our present university comes down to us from the middle ages. I will not say that at present it is a medi?val institution, but it had its roots in the middle ages, and it has not outlived all medi?val traditions regarding learning.
The kindergarten, rising with the present century, was a union of the nursery and of the philosophy of Schelling; a wedding of the plays and games which the mother carried on with her children, to Schelling’s highly romantic and symbolic15 philosophy. The elements that came from the actual study of child life—the continuation of the nursery—have remained a life-bringing force in all education; the Schellingesque factors made an obstruction16 between it and the rest of the school system, brought about isolations.
The line drawn17 over the top indicates that there is a certain interaction between the kindergarten and the primary school; for, so far as the primary school remained in spirit foreign to the natural interests of child life, it was isolated18 from the kindergarten, so that it is a problem, at present, to introduce kindergarten methods into the primary school; the problem of the so-called connecting class. The difficulty is that the two 82are not one from the start. To get a connection the teacher has had to climb over the wall instead of entering in at the gate.
On the side of aims, the ideal of the kindergarten was the moral development of the children, rather than instruction or discipline; an ideal sometimes emphasized to the point of sentimentality. The primary school grew practically out of the popular movement of the sixteenth century, when along with the invention of printing and the growth of commerce, it became a business necessity to know how to read, write, and figure. The aim was distinctly a practical one; it was utility; getting command of these tools, the symbols of learning, not for the sake of learning, but because they gave access to careers in life otherwise closed.
The division next to the primary school is the grammar school. The term is not much used in the West, but is common in the eastern states. It goes back to the time of the revival20 of learning—a little earlier perhaps than the conditions out of which the primary school originated, and, even when contemporaneous, having a different ideal. It had to do with the study of language in the higher sense; because, at the time of the Renaissance21, Latin and Greek connected people with the culture of the past, with the Roman and Greek world. The classic languages were the 83only means of escape from the limitations of the middle ages. Thus there sprang up the prototype of the grammar school, more liberal than the university (so largely professional in character), for the purpose of putting into the hands of the people the key to the old learning, that men might see a world with a larger horizon. The object was primarily culture, secondarily discipline. It represented much more than the present grammar school. It was the liberal element in the college, which, extending downward, grew into the academy and the high school. Thus the secondary school is still in part just a lower college (having an even higher curriculum than the college of a few centuries ago) or a preparatory department to a college, and in part a rounding up of the utilities of the elementary school.
There appear then two products of the nineteenth century, the technical and normal schools. The schools of technology, engineering, etc., are, of course, mainly the development of nineteenth-century business conditions, as the primary school was the development of business conditions of the sixteenth century. The normal school arose because of the necessity for training teachers, with the idea partly of professional drill, and partly that of culture.
Without going into more detail, we have 84some eight different parts of the school system as represented on the chart, all of which arose historically at different times, having different ideals in view, and consequently different methods. I do not wish to suggest that all of the isolation, all of the separation, that has existed in the past between the different parts of the school system still persists. One must, however, recognize that they have never yet been welded into one complete whole. The great problem in education on the administrative22 side is how to unite these different parts.
Consider the training schools for teachers—the normal schools. These occupy at present a somewhat anomalous23 position, intermediate between the high school and the college, requiring the high-school preparation, and covering a certain amount of college work. They are isolated from the higher subject-matter of scholarship, since, upon the whole, their object has been to train persons how to teach, rather than what to teach; while, if we go to the college, we find the other half of this isolation—learning what to teach, with almost a contempt for methods of teaching. The college is shut off from contact with children and youth. Its members, to a great extent, away from home and forgetting their own childhood, become eventually teachers with a large amount of subject-matter at command, and 85little knowledge of how this is related to the minds of those to whom it is to be taught. In this division between what to teach and how to teach, each side suffers from the separation.
It is interesting to follow out the inter-relation between primary, grammar, and high schools. The elementary school has crowded up and taken many subjects previously24 studied in the old New England grammar school. The high school has pushed its subjects down. Latin and algebra25 have been put in the upper grades, so that the seventh and eighth grades are, after all, about all that is left of the old grammar school. They are a sort of amorphous26 composite, being partly a place where children go on learning what they already have learned (to read, write, and figure), and partly a place of preparation for the high school. The name in some parts of New England for these upper grades was “Intermediate School.” The term was a happy one; the work was simply intermediate between something that had been and something that was going to be, having no special meaning on its own account.
Just as the parts are separated, so do the ideals differ—moral development, practical utility, general culture, discipline, and professional training. These aims are each especially represented in some distinct part of the system of education; 86and with the growing interaction of the parts, each is supposed to afford a certain amount of culture, discipline, and utility. But the lack of fundamental unity is witnessed in the fact that one study is still considered good for discipline, and another for culture; some parts of arithmetic, for example, for discipline and others for use, literature for culture, grammar for discipline, geography partly for utility, partly for culture; and so on. The unity of education is dissipated, and the studies become centrifugal; so much of this study to secure this end, so much of that to secure another, until the whole becomes a sheer compromise and patchwork27 between contending aims and disparate studies. The great problem in education on the administrative side is to secure the unity of the whole, in the place of a sequence of more or less unrelated and overlapping parts and thus to reduce the waste arising from friction28, reduplication and transitions that are not properly bridged.
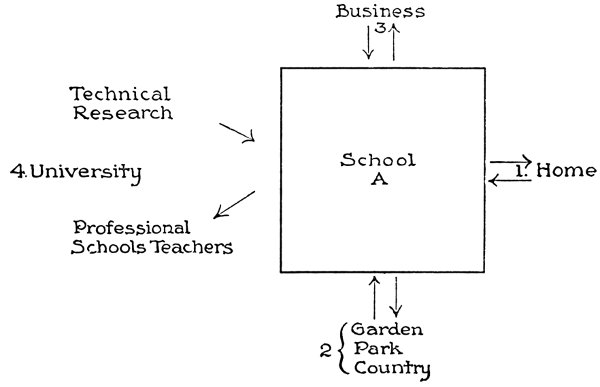
In this second symbolic diagram (II) I wish to suggest that really the only way to unite the parts of the system is to unite each to life. We can get only an artificial unity so long as we confine our gaze to the school system itself. We must look at it as part of the larger whole of social life. This block (A) in the center represents the school system as a whole. (1) At one side we have the 89home, and the two arrows represent the free interplay of influences, materials, and ideas between the home life and that of the school. (2) Below we have the relation to the natural environment, the great field of geography in the widest sense. The school building has about it a natural environment. It ought to be in a garden, and the children from the garden would be led on to surrounding fields, and then into the wider country, with all its facts and forces. (3) Above is represented business life, and the necessity for free play between the school and the needs and forces of industry. (4) On the other side is the university proper, with its various phases, its laboratories, its resources in the way of libraries, museums, and professional schools.
From the standpoint of the child, the great waste in the school comes from his inability to utilize29 the experiences he gets outside the school in any complete and free way within the school itself; while, on the other hand, he is unable to apply in daily life what he is learning at school. That is the isolation of the school—its isolation from life. When the child gets into the schoolroom he has to put out of his mind a large part of the ideas, interests, and activities that predominate in his home and neighborhood. So the school, being unable to utilize this everyday experience, sets painfully to work, on another tack30 and by a 90variety of means, to arouse in the child an interest in school studies. While I was visiting in the city of Moline a few years ago, the superintendent told me that they found many children every year, who were surprised to learn that the Mississippi river in the text-book had anything to do with the stream of water flowing past their homes. The geography being simply a matter of the schoolroom, it is more or less of an awakening31 to many children to find that the whole thing is nothing but a more formal and definite statement of the facts which they see, feel, and touch every day. When we think that we all live on the earth, that we live in an atmosphere, that our lives are touched at every point by the influences of the soil, flora32, and fauna33, by considerations of light and heat, and then think of what the school study of geography has been, we have a typical idea of the gap existing between the everyday experiences of the child, and the isolated material supplied in such large measure in the school. This is but an instance, and one upon which most of us may reflect long before we take the present artificiality of the school as other than a matter of course or necessity.
Though there should be organic connection between the school and business life, it is not meant that the school is to prepare the child for any particular business, but that there should be 91a natural connection of the everyday life of the child with the business environment about him, and that it is the affair of the school to clarify and liberalize this connection, to bring it to consciousness, not by introducing special studies, like commercial geography and arithmetic, but by keeping alive the ordinary bonds of relation. The subject of compound-business-partnership34 is probably not in many of the arithmetics nowadays, though it was there not a generation ago, for the makers35 of text-books said that if they left out anything they could not sell their books. This compound-business-partnership originated as far back as the sixteenth century. The joint-stock company had not been invented, and as large commerce with the Indies and Americas grew up, it was necessary to have an accumulation of capital with which to handle it. One man said, “I will put in this amount of money for six months,” and another, “So much for two years,” and so on. Thus by joining together they got money enough to float their commercial enterprises. Naturally, then, “compound partnership” was taught in the schools. The joint-stock company was invented; compound partnership disappeared, but the problems relating to it stayed in the arithmetics for two hundred years. They were kept after they had ceased to have practical utility, for the sake of mental discipline—they 92were “such hard problems, you know.” A great deal of what is now in the arithmetics under the head of percentage is of the same nature. Children of twelve and thirteen years of age go through gain and loss calculations, and various forms of bank discount so complicated that the bankers long ago dispensed36 with them. And when it is pointed37 out that business is not done this way, we hear again of “mental discipline.” And yet there are plenty of real connections between the experience of children and business conditions which need to be utilized38 and illuminated39. The child should study his commercial arithmetic and geography, not as isolated things by themselves, but in their reference to his social environment. The youth needs to become acquainted with the bank as a factor in modern life, with what it does, and how it does it; and then relevant arithmetical processes would have some meaning—quite in contradistinction to the time-absorbing and mind-killing examples in percentage, partial payments, etc., found in all our arithmetics.
The connection with the university, as indicated in this chart, I need not dwell upon. I simply wish to indicate that there ought to be a free interaction between all the parts of the school system. There is much of utter triviality of subject-matter in elementary and secondary 93education. When we investigate it, we find that it is full of facts taught that are not facts, which have to be unlearned later on. Now, this happens because the “lower” parts of our system are not in vital connection with the “higher.” The university or college, in its idea, is a place of research, where investigation40 is going on, a place of libraries and museums, where the best resources of the past are gathered, maintained and organized. It is, however, as true in the school as in the university that the spirit of inquiry41 can be got only through and with the attitude of inquiry. The pupil must learn what has meaning, what enlarges his horizon, instead of mere42 trivialities. He must become acquainted with truths, instead of things that were regarded as such fifty years ago, or that are taken as interesting by the misunderstanding of a partially43 educated teacher. It is difficult to see how these ends can be reached except as the most advanced part of the educational system is in complete interaction with the most rudimentary.
The next chart (III) is an enlargement of the second. The school building has swelled44 out, so to speak, the surrounding environment remaining the same, the home, the garden and country, the relation to business life and the university. The object is to show what the school must become to get out of its isolation and secure the organic 94connection with social life of which we have been speaking. It is not our architect’s plan for the school building that we hope to have; but it is a diagrammatic representation of the idea which we want embodied45 in the school building. On the lower side you see the dining-room and the kitchen, at the top the wood and metal shops, and the textile room for sewing and weaving. The center represents the manner in which all come together in the library; that is to say, in a collection of the intellectual resources of all kinds that throw light upon the practical work, that give it meaning and liberal value. If the four corners represent practice, the interior represents the theory of the practical activities. In other words, the object of these forms of practice in the school is not found chiefly in themselves, or in the technical skill of cooks, seamstresses, carpenters and masons, but in their connection, on the social side, with the life without; while on the individual side they respond to the child’s need of action, of expression, of desire to do something, to be constructive46 and creative, instead of simply passive and conforming. Their great significance is that they keep the balance between the social and individual sides—the chart symbolizing47 particularly the connection with the social. Here on one side is the home. How naturally the lines of connection play back and forth48 between the home 96and the kitchen and the textile room of the school! The child can carry over what he learns in the home and utilize it in the school; and the things learned in the school he applies at home. These are the two great things in breaking down isolation, in getting connection—to have the child come to school with all the experience he has got outside the school, and to leave it with something to be immediately used in his everyday life. The child comes to the traditional school with a healthy body and a more or less unwilling50 mind, though, in fact, he does not bring both his body and mind with him; he has to leave his mind behind, because there is no way to use it in the school. If he had a purely51 abstract mind, he could bring it to school with him, but his is a concrete one, interested in concrete things, and unless these things get over into school life, he cannot take his mind with him. What we want is to have the child come to school with a whole mind and a whole body, and leave school with a fuller mind and an even healthier body. And speaking of the body suggests that, while there is no gymnasium in these diagrams, the active life carried on in its four corners brings with it constant physical exercise, while our gymnasium proper will deal with the particular weaknesses of children and their correction, and will attempt more consciously to build up the 97thoroughly sound body as the abode52 of the sound mind.
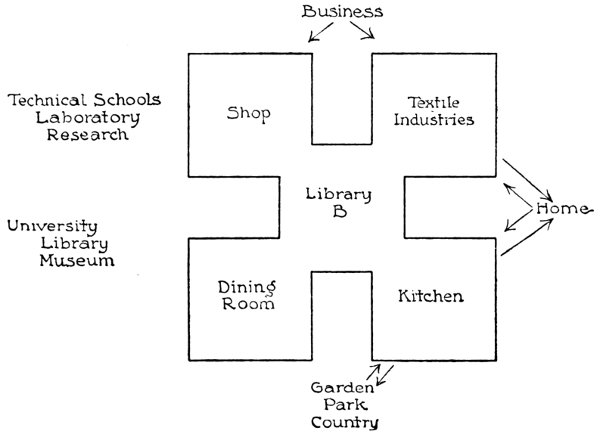
That the dining-room and kitchen connect with the country and its processes and products it is hardly necessary to say. Cooking may be so taught that it has no connection with country life, and with the sciences that find their unity in geography. Perhaps it generally has been taught without these connections being really made. But all the materials that come into the kitchen have their origin in the country; they come from the soil, are nurtured53 through the influences of light and water, and represent a great variety of local environments. Through this connection, extending from the garden into the larger world, the child has his most natural introduction to the study of the sciences. Where did these things grow? What was necessary to their growth? What their relation to the soil? What the effect of different climatic conditions? and so on. We all know what the old-fashioned botany was: partly collecting flowers that were pretty, pressing and mounting them; partly pulling these flowers to pieces and giving technical names to the different parts, finding all the different leaves, naming all their different shapes and forms. It was a study of plants without any reference to the soil, to the country, or to growth. In contrast, a real study of plants takes them in their natural 99environment and in their uses as well, not simply as food, but in all their adaptations to the social life of man. Cooking becomes as well a most natural introduction to the study of chemistry, giving the child here also something which he can at once bring to bear upon his daily experience. I once heard a very intelligent woman say that she could not understand how science could be taught to little children, because she did not see how they could understand atoms and molecules54. In other words, since she did not see how highly abstract facts could be presented to the child independently of daily experience, she could not understand how science could be taught at all. Before we smile at this remark, we need to ask ourselves if she is alone in her assumption, or whether it simply formulates55 almost all of our school practice.
The same relations with the outside world are found in the carpentry and the textile shops. They connect with the country, as the source of their materials, with physics, as the science of applying energy, with commerce and distribution, with art in the development of architecture and decoration. They have also an intimate connection with the university on the side of its technological56 and engineering schools; with the laboratory, and its scientific methods and results.
To go back to the square which is marked the 100library (Chart III, A): if you imagine rooms half in the four corners and half in the library, you will get the idea of the recitation room. That is the place where the children bring the experiences, the problems, the questions, the particular facts which they have found, and discuss them so that new light may be thrown upon them, particularly new light from the experience of others, the accumulated wisdom of the world—symbolized57 in the library. Here is the organic relation of theory and practice; the child not simply doing things, but getting also the idea of what he does; getting from the start some intellectual conception that enters into his practice and enriches it; while every idea finds, directly or indirectly58, some application in experience, and has some effect upon life. This, I need hardly say, fixes the position of the “book” or reading in education. Harmful as a substitute for experience, it is all-important in interpreting and expanding experience.
101The other chart (IV) illustrates59 precisely60 the same idea. It gives the symbolic upper story of this ideal school. In the upper corners are the laboratories; in the lower corners are the studios for art work, both the graphic61 and auditory arts. The questions, the chemical and physical problems, arising in the kitchen and shop, are taken to the laboratories to be worked out. For instance, this past week one of the older groups
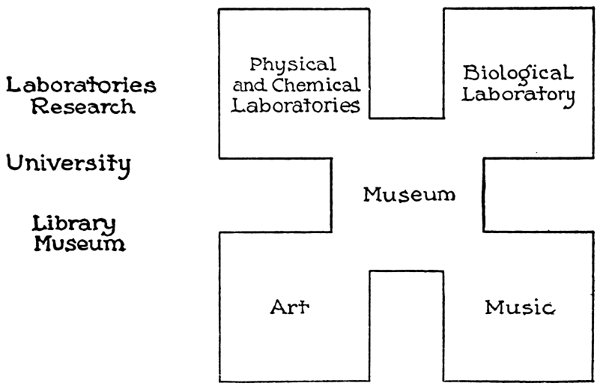
of children doing practical work in weaving which involved the use of the spinning wheel, worked out the diagrams of the direction of forces concerned in treadle and wheel, and the ratio of velocities62 between wheel and spindle. In the same manner, the plants with which the child has to do in cooking, afford the basis for a concrete interest in botany, and may be taken and studied by themselves. In a certain school in Boston science work for months was centered in the growth of the cotton plant, and yet something new was brought in every day. We hope to do similar work with all the types of plants that furnish materials for sewing and weaving. These examples will suggest, I hope, the relation which the laboratories bear to the rest of the school.
The drawing and music, or the graphic and auditory arts, represent the culmination63, the idealization, the highest point of refinement64 of all the work carried on. I think everybody who has not a purely literary view of the subject recognizes that genuine art grows out of the work of the artisan. The art of the Renaissance was great, because it grew out of the manual arts of life. It did not spring up in a separate atmosphere, however ideal, but carried on to their spiritual meaning processes found in homely65 and everyday forms of life. The school should observe this 104relationship. The merely artisan side is narrow, but the mere art, taken by itself, and grafted66 on from without, tends to become forced, empty, sentimental19. I do not mean, of course, that all art work must be correlated in detail to the other work of the school, but simply that a spirit of union gives vitality67 to the art, and depth and richness to the other work. All art involves physical organs, the eye and hand, the ear and voice; and yet it is something more than the mere technical skill required by the organs of expression. It involves an idea, a thought, a spiritual rendering68 of things; and yet it is other than any number of ideas by themselves. It is a living union of thought and the instrument of expression. This union is symbolized by saying that in the ideal school the art work might be considered to be that of the shops, passed through the alembic of library and museum into action again.
Take the textile room as an illustration of such a synthesis. I am talking about a future school, the one we hope, some time, to have. The basal fact in that room is that it is a workshop, doing actual things in sewing, spinning, and weaving. The children come into immediate49 connection with the materials, with various fabrics69 of silk, cotton, linen70 and wool. Information at once appears in connection with these materials; their origin, 105history, their adaptation to particular uses, and the machines of various kinds by which the raw materials are utilized. Discipline arises in dealing71 with the problems involved, both theoretical and practical. Whence does the culture arise? Partly from seeing all these things reflected through the medium of their scientific and historic conditions and associations, whereby the child learns to appreciate them as technical achievements, as thoughts precipitated72 in action; and partly because of the introduction of the art idea into the room itself. In the ideal school there would be something of this sort: first, a complete industrial museum, giving samples of materials in various stages of manufacture, and the implements73, from the simplest to the most complex, used in dealing with them; then a collection of photographs and pictures illustrating74 the landscapes and the scenes from which the materials come, their native homes, and their places of manufacture. Such a collection would be a vivid and continual lesson in the synthesis of art, science, and industry. There would be, also, samples of the more perfect forms of textile work, as Italian, French, Japanese, and Oriental. There would be objects illustrating motives75 of design and decoration which have entered into production. Literature would contribute its part in its idealized representation of the world-industries, as 106the Penelope in the Odyssey—a classic in literature only because the character is an adequate embodiment of a certain industrial phase of social life. So, from Homer down to the present time, there is a continuous procession of related facts which have been translated into terms of art. Music lends its share, from the Scotch76 song at the wheel to the spinning song of Marguerite, or of Wagner’s Senta. The shop becomes a pictured museum, appealing to the eye. It would have not only materials, beautiful woods and designs, but would give a synopsis77 of the historical evolution of architecture in its drawings and pictures.
Thus I have attempted to indicate how the school may be connected with life so that the experience gained by the child in a familiar, commonplace way is carried over and made use of there, and what the child learns in the school is carried back and applied78 in everyday life, making the school an organic whole, instead of a composite of isolated parts. The isolation of studies as well as of parts of the school system disappears. Experience has its geographical79 aspect, its artistic80 and its literary, its scientific and its historical sides. All studies arise from aspects of the one earth and the one life lived upon it. We do not have a series of stratified earths, one of which is mathematical, another physical, another historical, and so on. We 107should not live very long in any one taken by itself. We live in a world where all sides are bound together. All studies grow out of relations in the one great common world. When the child lives in varied81 but concrete and active relationship to this common world, his studies are naturally unified82. It will no longer be a problem to correlate studies. The teacher will not have to resort to all sorts of devices to weave a little arithmetic into the history lesson, and the like. Relate the school to life, and all studies are of necessity correlated.
Moreover, if the school is related as a whole to life as a whole, its various aims and ideals—culture, discipline, information, utility—cease to be variants83, for one of which we must select one study and for another another. The growth of the child in the direction of social capacity and service, his larger and more vital union with life, becomes the unifying84 aim; and discipline, culture and information fall into place as phases of this growth.
I wish to say one word more about the relationship of our particular school to the University. The problem is to unify85, to organize education, to bring all its various factors together, through putting it as a whole into organic union with everyday life. That which lies back of the pedagogical school of the University is the 108necessity of working out something to serve as a model for such unification, extending from work beginning with the four-year-old child up through the graduate work of the University. Already we have much help from the University in scientific work planned, sometimes even in detail, by heads of the departments. The graduate student comes to us with his researches and methods, suggesting ideas and problems. The library and museum are at hand. We want to bring all things educational together; to break down the barriers that divide the education of the little child from the instruction of the maturing youth; to identify the lower and the higher education, so that it shall be demonstrated to the eye that there is no lower and higher, but simply education.
Speaking more especially with reference to the pedagogical side of the work: I suppose the oldest university chair of pedagogy in our country is about twenty years old—that of the University of Michigan, founded in the latter seventies. But there are only one or two that have tried to make a connection between theory and practice. They teach for the most part by theory, by lectures, by reference to books, rather than through the actual work of teaching itself. At Columbia, through the Teachers’ College, there is an extensive and close connection between the University and the training of teachers. 109Something has been done in one or two other places along the same line. We want an even more intimate union here, so that the University shall put all its resources at the disposition86 of the elementary school, contributing to the evolution of valuable subject-matter and right method, while the school in turn will be a laboratory in which the student of education sees theories and ideas demonstrated, tested, criticised, enforced, and the evolution of new truths. We want the school in its relation to the University to be a working model of a unified education.
A word as to the relation of the school to educational interests generally. I heard once that the adoption87 of a certain method in use in our school was objected to by a teacher on this ground: “You know that it is an experimental school. They do not work under the same conditions that we are subject to.” Now, the purpose of performing an experiment is that other people need not experiment; at least need not experiment so much, may have something definite and positive to go by. An experiment demands particularly favorable conditions in order that results may be reached both freely and securely. It has to work unhampered, with all the needed resources at command. Laboratories lie back of all the great business enterprises of today, back of every great factory, 110every railway and steamship88 system. Yet the laboratory is not a business enterprise; it does not aim to secure for itself the conditions of business life, nor does the commercial undertaking89 repeat the laboratory. There is a difference between working out and testing a new truth, or a new method, and applying it on a wide scale, making it available for the mass of men, making it commercial. But the first thing is to discover the truth, to afford all necessary facilities, for this is the most practical thing in the world in the long run. We do not expect to have other schools literally90 imitate what we do. A working model is not something to be copied; it is to afford a demonstration91 of the feasibility of the principle, and of the methods which make it feasible. So (to come back to our own point) we want here to work out the problem of the unity, the organization of the school system in itself, and to do this by relating it so intimately to life as to demonstrate the possibility and necessity of such organization for all education.

点击 收听单词发音
收听单词发音
 收听单词发音
收听单词发音
1
briefly

|
|
| adv.简单地,简短地 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
2
motive

|
|
| n.动机,目的;adv.发动的,运动的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
3
promotion

|
|
| n.提升,晋级;促销,宣传 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
4
afterward

|
|
| adv.后来;以后 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
5
inadequate

|
|
| adj.(for,to)不充足的,不适当的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
6
perverted

|
|
| adj.不正当的v.滥用( pervert的过去式和过去分词 );腐蚀;败坏;使堕落 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
7
superintendent

|
|
| n.监督人,主管,总监;(英国)警务长 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
8
unity

|
|
| n.团结,联合,统一;和睦,协调 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
9
isolation

|
|
| n.隔离,孤立,分解,分离 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
10
fully

|
|
| adv.完全地,全部地,彻底地;充分地 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
11
coherence

|
|
| n.紧凑;连贯;一致性 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
12
illustrate

|
|
| v.举例说明,阐明;图解,加插图 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
13
overlapping

|
|
| adj./n.交迭(的) | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
14
essentially

|
|
| adv.本质上,实质上,基本上 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
15
symbolic

|
|
| adj.象征性的,符号的,象征主义的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
16
obstruction

|
|
| n.阻塞,堵塞;障碍物 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
17
drawn

|
|
| v.拖,拉,拔出;adj.憔悴的,紧张的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
18
isolated

|
|
| adj.与世隔绝的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
19
sentimental

|
|
| adj.多愁善感的,感伤的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
20
revival

|
|
| n.复兴,复苏,(精力、活力等的)重振 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
21
renaissance

|
|
| n.复活,复兴,文艺复兴 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
22
administrative

|
|
| adj.行政的,管理的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
23
anomalous

|
|
| adj.反常的;不规则的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
24
previously

|
|
| adv.以前,先前(地) | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
25
algebra

|
|
| n.代数学 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
26
amorphous

|
|
| adj.无定形的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
27
patchwork

|
|
| n.混杂物;拼缝物 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
28
friction

|
|
| n.摩擦,摩擦力 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
29
utilize

|
|
| vt.使用,利用 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
30
tack

|
|
| n.大头钉;假缝,粗缝 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
31
awakening

|
|
| n.觉醒,醒悟 adj.觉醒中的;唤醒的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
32
flora

|
|
| n.(某一地区的)植物群 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
33
fauna

|
|
| n.(一个地区或时代的)所有动物,动物区系 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
34
partnership

|
|
| n.合作关系,伙伴关系 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
35
makers

|
|
| n.制造者,制造商(maker的复数形式) | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
36
dispensed

|
|
| v.分配( dispense的过去式和过去分词 );施与;配(药) | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
37
pointed

|
|
| adj.尖的,直截了当的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
38
utilized

|
|
| v.利用,使用( utilize的过去式和过去分词 ) | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
39
illuminated

|
|
| adj.被照明的;受启迪的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
40
investigation

|
|
| n.调查,调查研究 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
41
inquiry

|
|
| n.打听,询问,调查,查问 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
42
mere

|
|
| adj.纯粹的;仅仅,只不过 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
43
partially

|
|
| adv.部分地,从某些方面讲 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
44
swelled

|
|
| 增强( swell的过去式和过去分词 ); 肿胀; (使)凸出; 充满(激情) | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
45
embodied

|
|
| v.表现( embody的过去式和过去分词 );象征;包括;包含 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
46
constructive

|
|
| adj.建设的,建设性的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
47
symbolizing

|
|
| v.象征,作为…的象征( symbolize的现在分词 ) | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
48
forth

|
|
| adv.向前;向外,往外 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
49
immediate

|
|
| adj.立即的;直接的,最接近的;紧靠的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
50
unwilling

|
|
| adj.不情愿的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
51
purely

|
|
| adv.纯粹地,完全地 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
52
abode

|
|
| n.住处,住所 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
53
nurtured

|
|
| 养育( nurture的过去式和过去分词 ); 培育; 滋长; 助长 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
54
molecules

|
|
| 分子( molecule的名词复数 ) | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
55
formulates

|
|
| v.构想出( formulate的第三人称单数 );规划;确切地阐述;用公式表示 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
56
technological

|
|
| adj.技术的;工艺的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
57
symbolized

|
|
| v.象征,作为…的象征( symbolize的过去式和过去分词 ) | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
58
indirectly

|
|
| adv.间接地,不直接了当地 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
59
illustrates

|
|
| 给…加插图( illustrate的第三人称单数 ); 说明; 表明; (用示例、图画等)说明 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
60
precisely

|
|
| adv.恰好,正好,精确地,细致地 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
61
graphic

|
|
| adj.生动的,形象的,绘画的,文字的,图表的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
62
velocities

|
|
| n.速度( velocity的名词复数 );高速,快速 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
63
culmination

|
|
| n.顶点;最高潮 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
64
refinement

|
|
| n.文雅;高尚;精美;精制;精炼 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
65
homely

|
|
| adj.家常的,简朴的;不漂亮的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
66
grafted

|
|
| 移植( graft的过去式和过去分词 ); 嫁接; 使(思想、制度等)成为(…的一部份); 植根 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
67
vitality

|
|
| n.活力,生命力,效力 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
68
rendering

|
|
| n.表现,描写 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
69
fabrics

|
|
| 织物( fabric的名词复数 ); 布; 构造; (建筑物的)结构(如墙、地面、屋顶):质地 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
70
linen

|
|
| n.亚麻布,亚麻线,亚麻制品;adj.亚麻布制的,亚麻的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
71
dealing

|
|
| n.经商方法,待人态度 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
72
precipitated

|
|
| v.(突如其来地)使发生( precipitate的过去式和过去分词 );促成;猛然摔下;使沉淀 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
73
implements

|
|
| n.工具( implement的名词复数 );家具;手段;[法律]履行(契约等)v.实现( implement的第三人称单数 );执行;贯彻;使生效 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
74
illustrating

|
|
| 给…加插图( illustrate的现在分词 ); 说明; 表明; (用示例、图画等)说明 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
75
motives

|
|
| n.动机,目的( motive的名词复数 ) | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
76
scotch

|
|
| n.伤口,刻痕;苏格兰威士忌酒;v.粉碎,消灭,阻止;adj.苏格兰(人)的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
77
synopsis

|
|
| n.提要,梗概 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
78
applied

|
|
| adj.应用的;v.应用,适用 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
79
geographical

|
|
| adj.地理的;地区(性)的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
80
artistic

|
|
| adj.艺术(家)的,美术(家)的;善于艺术创作的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
81
varied

|
|
| adj.多样的,多变化的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
82
unified

|
|
| (unify 的过去式和过去分词); 统一的; 统一标准的; 一元化的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
83
variants

|
|
| n.变体( variant的名词复数 );变种;变型;(词等的)变体 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
84
unifying

|
|
| 使联合( unify的现在分词 ); 使相同; 使一致; 统一 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
85
unify

|
|
| vt.使联合,统一;使相同,使一致 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
86
disposition

|
|
| n.性情,性格;意向,倾向;排列,部署 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
87
adoption

|
|
| n.采用,采纳,通过;收养 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
88
steamship

|
|
| n.汽船,轮船 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
89
undertaking

|
|
| n.保证,许诺,事业 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
90
literally

|
|
| adv.照字面意义,逐字地;确实 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
91
demonstration

|
|
| n.表明,示范,论证,示威 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
| 欢迎访问英文小说网 |

