Chap. ii.
On the Magnetick Coition, and first on the Attraction of Amber1, or more truly, on the Attaching of Bodies to Amber.
C elebrated has the fame of the loadstone and of amber ever been in the memoirs2 of the learned. Loadstone and also amber do some philosophers invoke3 when in explaining many secrets their senses become dim and reasoning cannot go further. Inquisitive4 theologians also would throw light on the divine mysteries set beyond the range of human sense, by means of loadstone and amber; just as idle Metaphysicians, when they are setting up and teaching useless phantasms, have recourse to the loadstone as if it were a Delphick sword, an illustration always applicable to everything. But physicians even (with the authority of Galen), desiring to confirm the belief in the attraction of purgative5 medicines by means of the likeness6 of substance and the familiarities of the juices — truly a vain and useless error — bring in the loadstone as witness as being a nature of great authority and of conspicuous8 efficacy and a remarkable9 body. So in very many cases there are some who, when they are pleading a cause and cannot give a reason for it, bring in loadstone and amber as though they were personified witnesses. But these men (apart from that common error) being ignorant that the causes of magnetical motions are widely different from the forces of amber, easily fall into error, and are themselves the more deceived by their own cogitations. For in other bodies a conspicuous force of attraction manifests itself otherwise than in loadstone; like as in amber, concerning which some things must first be said, that it may appear what is that attaching of bodies, and how it is different from and foreign to the magnetical actions; those mortals being still ignorant, who think that inclination10 to be an attraction, and compare it with the magnetick coitions. The Greeks call it ἤλεκτρον108 because it attracts straws to itself, when it is warmed by rubbing; then it is called ἅρπαξ109; and χρυσοφόρον from its golden colour. But the Moors11 call it Carabe110, because they are accustomed to offer the same in sacrifices and in the worship of the Gods. For Carab signifies to offer in Arabic; so Carabe, an offering: or seizing chaff12, as Scaliger quotes from Abohalis, out of the Arabic or Persian language. Some also call it Amber, especially the Indian and Ethiopian amber, called in Latin Succinum, as if it were a juice111. The Sudavienses or Sudini112 call it geniter, as though it were generated terrestrially. The errors of the ancients concerning its nature and origin having been exploded, it is certain that amber comes for the most part from the sea, and the rustics13 collect it on the coast after the more violent storms, with nets and other tackle; as among the Sudini of Prussia; and it is also found sometimes on the coast of our own Britain. It seems, however, to be produced also in the soil and at spots of some depth, like other bitumens; to be washed out by the waves of the sea; and to become concreted more firmly from the nature and saltness of the sea-water. For it was at first a soft and viscous15 material; wherefore also it contains enclosed and entombed in pieces of it, shining in eternal sepulchres, flies, grubs, gnats16, ants; which have all flown or crept or fallen into it when it first flowed forth17 in a liquid state113. The ancients and also more recent writers recall (experience proving the same thing), that amber attracts straws and chaff114. The same is also done by jet115, which is dug out of the earth in Britain, in Germany, and in very many lands, and is a rather hard concretion from black bitumen14, and as it were a transformation18 into stone. There are many modern authors116 who have written and copied from others about amber and jet117 attracting chaff, and about other substances generally unknown; with whose labours the shops of booksellers are crammed19. Our own age has produced many books about hidden, abstruse20, and occult causes and wonders, in all of which amber and jet are set forth as enticing21 chaff; but they treat the subject in words alone, without finding any reasons or proofs from experiments, their very statements obscuring the thing in a greater fog, forsooth in a cryptic23, marvellous, abstruse, secret, occult, way. Wherefore also such philosophy produces no fruit, because very many philosophers, making no investigation25 themselves, unsupported by any practical experience, idle and inert26, make no progress by their records, and do not see what light they can bring to their theories; but their philosophy rests simply on the use of certain Greek words, or uncommon27 ones; after the manner of our gossips and barbers nowadays, who make show of certain Latin words to an ignorant populace as the insignia of their craft, and snatch at the popular favour. For it is not only amber and jet (as they suppose) which entice28 small bodies118; but Diamond, Sapphire29, Carbuncle, Iris30 gem119, Opal, Amethyst32, Vincentina, and Bristolla (an English gem31 or spar)120, Beryl, and Crystal121 do the same. Similar powers of attraction are seen also to be possessed33 by glass (especially when clear and lucid34), as also by false gems35 made of glass or Crystal, by glass of antimony, and by many kinds of spars from the mines, and by Belemnites. Sulphur also attracts, and mastick, and hard sealing-wax122 compounded of lac tinctured of various colours. Rather hard resin36 entices37, as does orpiment123, but less strongly; with difficulty also and indistinctly under a suitable dry sky124, Rock salt, muscovy stone, and rock alum. This one may see when the air is sharp and clear and rare in mid-winter, when the emanations from the earth hinder electricks less, and the electrick bodies become more firmly indurated; about which hereafter. These substances draw everything, not straws and chaff only125, but all metals, woods, leaves, stones, earths, even water and oil, and everything which is subject to our senses, or is solid; although some write that amber does not attract anything but chaff and certain twigs38; (wherefore Alexander Aphrodiseus falsely declares the question of amber to be inexplicable39, because it attracts dry chaff only, and not basil leaves126), but these are the utterly40 false and disgraceful tales of the writers. But in order that you may be able clearly to test how such attraction occurs127, and what those materials128 are which thus entice other bodies (for even if bodies incline towards some of these, yet on account of weakness they seem not to be raised by them, but are more easily turned), make yourself a versorium of any metal you like, three or four digits41 in length, resting rather lightly on its point of support after the manner of a magnetick needle, to one end of which bring up a piece of
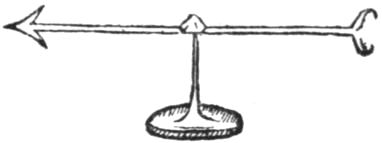
amber or a smooth . and polished gem which has been gently rubbed; for the versorium turns forthwith. Many things are thereby42 seen to attract, both those which are formed by nature alone, and those which are by art prepared, fused, and mixed; nor is this so much a singular property of one or two things (as is commonly supposed), but the manifest nature of very many, both of simple substances, remaining merely in their own form, and of compositions, as of hard sealing-wax, & of certain other mixtures besides, made of unctuous43 stuffs. We must, however, investigate more fully44 whence that tendency arises, and what those forces be, concerning which a few men have brought forward very little, the crowd of philosophizers nothing at all. By Galen three kinds of attractives in general were recognized in nature: a First class of those substances which attract by their elemental quality, namely, heat; the Second is the class of those which attract by the succession of a vacuum; the Third is the class of those which attract by a property of their whole substance, which are also quoted by Avicenna and others. These classes, however, cannot in any way satisfy us; they neither embrace the causes of amber, jet, and diamond, and of other similar substances (which derive45 their forces on account of the same virtue46); nor of the loadstone, and of all magnetick substances, which obtain their virtue by a very dissimilar and alien influence from them, derived47 from other sources. Wherefore also it is fitting that we find other causes of the motions, or else we must wander (as in darkness), with these men, and in no way reach the goal. Amber truly does not allure48 by heat, since if warmed by fire and brought near straws, it does not attract them, whether it be tepid49, or hot, or glowing, or even when forced into the flame. Cardan (as also Pictorio) reckons that this happens in no different way129 than with the cupping-glass, by the force of fire. Yet the attracting force of the cupping-glass does not really come from the force of fire. But he had previously50 said that the dry substance wished to imbibe51 fatty humour, and therefore it was borne towards it. But these statements are at variance52 with one another, and also foreign to reason. For if amber had moved towards its food, or if other bodies had inclined towards amber as towards provender53, there would have been a diminution54 of the one which was devoured55, just as there would have been a growth of the other which was sated. Then why should an attractive force of fire be looked for in amber? If the attraction existed from heat, why should not very many other bodies also attract, if warmed by fire, by the sun, or by friction56? Neither can the attraction be on account of the dissipating of the air, when it takes place in open air (yet Lucretius the poet adduces this as the reason for magnetical motions). Nor in the cupping-glass can heat or fire attract by feeding on air: in the cupping-glass air, having been exhausted57 into flame, when it condenses again and is forced into a narrow space, makes the skin and flesh rise in avoiding a vacuum. In the open air warm things cannot attract, not metals even or stones, if they should be strongly incandescent58 by fire. For a rod of glowing iron, or a flame, or a candle, or a blazing torch, or a live coal, when they are brought near to straws, or to a versorium, do not attract; yet at the same time they manifestly call in the air in succession; because they consume it, as lamps do oil. But concerning heat, how it is reckoned by the crowd of philosophizers, in natural philosophy and in materia medica to exert an attraction otherwise than nature allows, to which true attractions are falsely imputed59, we will discuss more at length elsewhere, when we shall determine what are the properties of heat and cold. They are very general qualities or kinships of a substance, and yet are not to be assigned as true causes, and, if I may say so, those philosophizers utter some resounding60 words; but about the thing itself prove nothing in particular. Nor does this attraction accredited61 to amber arise from any singular quality of the substance or kinship, since by more thorough research we find the same effect in very many other bodies; and all bodies, moreover, of whatever quality, are allured62 by all those bodies. Similarity also is not the cause; because all things around us placed on this globe of the earth, similar and dissimilar, are allured by amber and bodies of this kind; and on that account no cogent63 analogy is to be drawn64 either from similarity or identity of substance. But neither do similars mutually attract one another, as stone stone, flesh flesh, nor aught else outside the class of magneticks and electricks. Fracastorio would have it that "things which mutually attract one another are similars, as being of the same species, either in action or in right subjection. Right subjection is that from which is emitted the emanation which attracts and which in mixtures often lies hidden on account of their lack of form, by reason of which they are often different in act from what they are in potency66. Hence it may be that hairs and twigs move towards amber and towards diamond, not because they are hairs, but because either there is shut up in them air or some other principle, which is attracted in the first place, and which bears some relation and analogy to that which attracts of itself; in which diamond and amber agree through a principle common to each." Thus far Fracastorio. Who if he had observed by a large number of experiments that all bodies are drawn to electricks except those which are aglow67 and aflame, and highly rarefied, would never have given a thought to such things. It is easy for men of acute intellect, apart from experiments and practice, to slip and err7. In greater error do they remain sunk who maintain these same substances to be not similar, but to be substances near akin24; and hold that on that account a thing moves towards another, its like, by which it is brought to more perfection. But these are ill-considered views; for towards all electricks all things move130 except such as are aflame or are too highly rarefied, as air, which is the universal effluvium of this globe and of the world. Vegetable substances draw moisture by which their shoots are rejoiced and grow; from analogy with that, however, Hippocrates, in his De Natura Hominis, Book I., wrongly concluded that the purging68 of morbid69 humour took place by the specifick force of the drug. Concerning the action and potency of purgatives70 we shall speak elsewhere. Wrongly also is attraction inferred in other effects; as in the case of a flagon full of water, when buried in a heap of wheat, although well stoppered, the moisture is drawn out; since this moisture is rather resolved into vapour by the emanation of the fermenting71 wheat, and the wheat imbibes72 the freed vapour. Nor do elephants' tusks73 attract moisture, but drive it into vapour or absorb it. Thus then very many things are said to attract, the reasons for whose energy must be sought from other causes. Amber in a fairly large mass allures74, if it is polished; in a smaller mass or less pure it seems not to attract without friction. But very many electricks (as precious stones and some other substances) do not attract at all unless rubbed. On the other hand many gems, as well as other bodies, are polished, yet do not allure, and by no amount of friction are they aroused; thus the emerald, agate75, carnelian, pearls, jasper, chalcedony, alabaster76, porphyry, coral, the marbles, touchstone, flint, bloodstone, emery131, do not acquire any power; nor do bones, or ivory, or the hardest woods, as ebony, nor do cedar77, juniper, or cypress78; nor do metals, silver, gold, brass79, iron, nor any loadstone, though many of them are finely polished and shine. But on the other hand there are some other polished substances of which we have spoken before, toward which, when they have been rubbed, bodies incline. This we shall understand only when we have more closely looked into the prime origin of bodies. It is plain to all, and all admit, that the mass of the earth, or rather the structure and crust of the earth, consists of a twofold material, namely, of fluid and humid matter, and of material of more consistency80 and dry. From this twofold nature or the more simple compacting of one, various substances take their rise among us, which originate in greater proportion now from the earthy, now from the aqueous nature. Those substances which have received their chief growth from moisture, whether aqueous or fatty, or have taken on their form by a simpler compacting from them, or have been compacted from these same materials in long ages, if they have a sufficiently81 firm hardness, if rubbed after they have been polished and when they remain bright with the friction — towards those substances everything, if presented to them in the air, turns, if its too heavy weight does not prevent it. For amber has been compacted of moisture, and jet also. Lucid gems are made of water; just as Crystal132, which has been concreted from clear water, not always by a very great cold, as some used to judge, and by very hard frost, but sometimes by a less severe one, the nature of the soil fashioning it, the humour or juices being shut up in definite cavities, in the way in which spars are produced in mines. So clear glass is fused out of sand, and from other substances, which have their origin in humid juices. But the dross82 of metals, as also metals, stones, rocks, woods, contain earth rather, or are mixed with a good deal of earth; and therefore they do not attract. Crystal, mica83, glass, and all electricks do not attract if they are burnt or roasted; for their primordial84 supplies of moisture perish by heat, and are changed and exhaled85. All things therefore which have sprung from a predominant moisture and are firmly concreted, and retain the appearance of spar and its resplendent nature in a firm and compact body, allure all bodies, whether humid or dry. Those, however, which partake of the true earth-substance or are very little different from it, are seen to attract also, but from a far different reason, and (so to say) magnetically; concerning these we intend to speak afterwards. But those substances which are more mixed of water and earth, and are produced by the equal degradation87 of each element (in which the magnetick force of the earth is deformed88 and remains89 buried; while the watery90 humour, being fouled92 by joining with a more plentiful93 supply of earth, has not concreted in itself but is mingled94 with earthy matter), can in no way of themselves attract or move from its place anything which they do not touch. On this account metals, marbles, flints, woods, herbs, flesh, and very many other things can neither allure nor solicit95 any body either magnetically or electrically. (For it pleases us to call that an electrick force, which hath its origin from the humour.) But substances consisting mostly of humour, and which are not very firmly compacted by nature (whereby do they neither bear rubbing, but either melt down and become soft, or are not levigable, such as pitch, the softer kinds of resin, camphor, galbanum, ammoniack133, storax, asafœtida, benzoin, asphaltum, especially in rather warm weather) towards them small bodies are not borne; for without rubbing most electricks do not emit their peculiar96 and native exhalation and effluvium. The resin turpentine when liquid does not attract; for it cannot be rubbed; but if it has hardened into a mastick it does attract. But now at length we must understand why small bodies turn towards those substances which have drawn their origin from water; by what force and with what hands (so to speak) electricks seize upon kindred natures. In all bodies in the world two causes or principles have been laid down, from which the bodies themselves were produced, matter and form134. Electrical motions become strong from matter, but magnetick from form chiefly; and they differ widely from one another and turn out unlike, since the one is ennobled by numerous virtues97 and is prepotent; the other is ignoble98 and of less potency, and mostly restrained, as it were, within certain barriers; and therefore that force must at times be aroused by attrition or friction, until it is at a dull heat and gives off an effluvium and a polish is induced on the body. For spent air, either blown out of the mouth or given off from moister air, chokes the virtue. If indeed either a sheet of paper or a piece of linen99 be interposed, there will be no movement. But a loadstone, without friction or heat, whether dry or suffused100 with moisture, as well in air as in water, invites magneticks, even with the most solid bodies interposed, even planks101 of wood or pretty thick slabs102 of stone or sheets of metal. A loadstone appeals to magneticks only; towards electricks all things move. A loadstone135 raises great weights; so that if there is a loadstone weighing two ounces and strong, it attracts half an ounce or a whole ounce. An electrical substance only attracts very small weights; as, for instance, a piece of amber of three ounces weight, when rubbed, scarce raises a fourth part of a grain of barley103. But this attraction of amber and of electrical substances must be further investigated; and since there is this particular affection of matter, it may be asked why is amber rubbed, and what affection is produced by the rubbing, and what causes arise which make it lay hold on everything? As a result of friction it grows slightly warm and becomes smooth; two results which must often occur together. A large polished fragment of amber or jet attracts indeed, even without friction, but less strongly; but if it be brought gently near a flame or a live coal, so that it equally becomes warm, it does not attract small bodies because it is enveloped104 in a cloud from the body of the flaming substance, which emits a hot breath, and then impinges upon it vapour from a foreign body which for the most part is at variance with the nature of amber. Moreover the spirit of the amber which is called forth is enfeebled by alien heat; wherefore it ought not to have heat excepting that produced by motion only and friction, and, as it were, its own, not sent into it by other bodies. For as the igneous105 heat emitted from any burning substance cannot be so used that electricks may acquire their force from it; so also heat from the solar rays does not fit an electrick by the loosening of its right material, because it dissipates rather and consumes it (albeit a body which has been rubbed retains its virtue longer exposed to the rays of the sun than in the shade; because in the shade the effluvia are condensed to a greater degree and more quickly). Then again the fervour from the light of the Sun aroused by means of a burning mirror confers no vigour106 on the heated amber136; indeed it dissipates and corrupts107 all the electrick effluvia. Again, burning sulphur and hard wax, made from shell-lac, when aflame do not allure; for heat from friction resolves bodies into effluvia, which flame consumes away. For it is impossible for solid electricks to be resolved into their own true effluvia otherwise than by attrition, save in the case of certain substances which by reason of innate108 vigour emit effluvia constantly. They are rubbed with bodies which do not befoul their surface, and which produce a polish, as pretty stiff silk or a rough wool rag which is as little soiled as possible, or the dry palm. Amber also is rubbed with amber, with diamond, and with glass, and numerous other substances. Thus are electricks manipulated. These things being so, what is it which moves? Is it the body itself, inclosed within its own circumference109? Or is it something imperceptible to us, which flows out from the substance into the ambient air? Somewhat as Plutarch opines, saying in his Quæstiones Platonicæ137: That there is in amber something flammable or something having the nature of breath, and this by the attrition of the surface being emitted from its relaxed pores attracts bodies. And if it be an effusion does it seize upon the air whose motion the bodies follow, or upon the bodies themselves? But if amber allured the body itself, then what need were there of friction, if it is bare and smooth? Nor does the force arise from the light which is reflected from a smooth and polished body; for a Gem of Vincent's rock138, Diamond, and clear glass, attract when they are rough; but not so powerfully and quickly, because they are not so readily cleansed110 from extraneous111 moisture on the surface, and are not rubbed equally so as to be copiously112 resolved at that part. Nor does the sun by its own beams of light and its rays, which are of capital importance in nature, attract bodies in this way; and yet the herd113 of philosophizers considers that humours are attracted by the sun, when it is only denser114 humours that are being turned into thinner, into spirit and air; and so by the motion of effusion they ascend115 into the upper regions, or the attenuated116 exhalations are raised up from the denser air. Nor does it seem to take place from the effluvia attenuating117 the air, so that bodies impelled118 by the denser air penetrate120 towards the source of the rarefaction; in this case both hot and flaming bodies would also allure other bodies; but not even the lightest chaff, or any versorium moves towards a flame. If there is a flow and rush of air towards the body, how can a small diamond of the size of a pea139 summon towards itself so much air, that it seizes hold of a biggish long body placed in equilibrio (the air about one or other very small part of an end being attracted)? It ought also to have slopped or moved more slowly, before it came into contact with the body, especially if the piece of amber was rather broad and flat, from the accumulation of air on the surface of the amber and its flowing back again. If it is because the effluvia are thinner, and denser vapours come in return, as in breathing, then the body would rather have had a motion toward the electrick a little while after the beginning of the application; but when electricks which have been rubbed are applied121 quickly to a versorium then especially at once they act on the versorium, and it is attracted more when near them. But if it is because the rarefied effluvia produce a rarefied medium, and on that account bodies are more prone122 to slip down from a denser to a more attenuated medium; they might have been carried from the side in this way or downwards123, but not to bodies above them; or the attraction and apprehension124 of contiguous bodies would have been momentary125 only. But with a single friction jet and amber draw and attract bodies to them strongly and for a long time, sometimes for the twelfth part of an hour, especially in clear weather. But if the mass of amber be rather large, and the surface polished, it attracts without friction. Flint is rubbed and emits by attrition an inflammable matter that turns into sparks and heat. Therefore the denser effluvia of flint producing fire are very far different from electrical effluvia, which on account of their extreme attenuation126 do not take fire, nor are fit material for flame. Those effluvia are not of the nature of breath, for when emitted they do not propel anything, but are exhaled without sensible resistance and touch bodies. They are highly attenuated humours much more subtile than the ambient air; and in order that they may occur, bodies are required produced from humour and concreted with a considerable degree of hardness. Non-electrick bodies are not resolved into humid effluvia, and those effluvia mix with the common and general effluvia of the earth, and are not peculiar. Also besides the attraction of bodies, they retain them longer. It is probable therefore that amber does exhale86 something peculiar to itself, which allures bodies themselves, not the intermediate air. Indeed it plainly does draw the body itself in the case of a spherical127 drop of water standing128 on a dry surface; for a piece of amber applied to it at a suitable distance pulls the nearest parts out of their position and draws it up into a cone129; otherwise, if it were drawn by means of the air rushing along, the whole drop would have moved. That it does not attract the air is thus demonstrated: take a very thin wax candle, which makes a very small and clear flame; bring up to this, within two digits or any convenient distance, a piece of amber or jet, a broad flat piece, well prepared and skilfully130 rubbed, such a piece of amber as would attract bodies far and wide, yet it does not disturb the flame; which of necessity would have occurred, if the air was disturbed, for the flame would have followed the current of air. As far as the effluvia are sent out, so far it allures; but as a body approaches, its motion is accelerated, stronger forces drawing it; as also in the case of magneticks and in all natural motion; not by attenuating or by expelling the air, so that the body moves down into the place of the air which has gone out140; for thus it would have allured only and would not have retained; since it would at first also have repelled131 approaching bodies just as it drives the air itself; but indeed a particle, be it ever so small, does not avoid the first application made very quickly after rubbing. An effluvium exhales132 from amber and is emitted by rubbing: pearls, carnelian, agate, jasper, chalcedony, coral, metals, and other substances of that kind, when they are rubbed, produce no effect. Is there not also something which is exhaled from them by heat and attrition? Most truly; but from grosser bodies more blended with the earthy nature, that which is exhaled is gross and spent; for even towards very many electricks, if they are rubbed too hard, there is produced but a weak attraction of bodies, or none at all; the attraction is best when the rubbing has been gentle and very quick; for so the finest effluvia are evoked133. The effluvia arise from the subtile diffusion134 of humour, not from excessive and turbulent violence; especially in the case of those substances which have been compacted from unctuous matter, which when the atmosphere is very thin, when the North winds, and amongst us (English) the East winds, are blowing, have a surer and firmer effect, but during South winds and in damp weather, only a weak one; so that those substances which attract with difficulty in clear weather, in thick weather produce no motion at all; both because in grosser air lighter135 substances move with greater difficulty; and especially because the effluvia are stifled136, and the surface of the body that has been rubbed is affected137 by the spent humour of the air, and the effluvia are stopped at their very starting. On that account in the case of amber, jet, and sulphur, because they do not so easily take up moist air on their surface and are much more plenteously set free, that force is not so quickly suppressed as in gems, crystal, glass, and substances of that kind which collect on their surface the moister breath which has grown heavy. But it may be asked why does amber allure water, when water placed on its surface removes its action? Evidently because it is one thing to suppress it at its very start, and quite another to extinguish it when it has been emitted. So also thin and very fine silk, in common language Sarcenet, placed quickly on the amber, after it has been rubbed, hinders the attraction of the body; but if it is interposed in the intervening space, it does not entirely138 obstruct139 it. Moisture also from spent air, and any breath blown from the mouth, as well as water put on the amber, immediately extinguishes its force. But oil, which is light and pure, does not hinder it; for although amber be rubbed with a warm finger dipped in oil, still it attracts. But if that amber, after the rubbing, is moistened with aqua vitæ or spirits of wine, it does not attract; for it is heavier than oil, denser, and when added to oil sinks beneath it. For oil is light and rare, and does not resist the most delicate effluvia. A breath therefore, proceeding140 from a body which had been compacted from humour or from a watery liquid, reaches the body to be attracted; the body that is reached is united with the attracting body, and the one body lying near the other within the peculiar radius141 of its effluvia makes one out of two; united, they come together into the closest accord, and this is commonly called attraction. This unity142, according to the opinion of Pythagoras, is the principle of all things, and through participation143 in it each several thing is said to be one. For since no action can take place by means of matter unless by contact, these electricks are not seen to touch, but, as was necessary, something is sent from the one to the other, something which may touch closely and be the beginning of that incitement144. All bodies are united and, as it were, cemented together in some way by moisture; so that a wet body, when it touches another body, attracts it, if it is small. So wet bodies on the surface of water attract wet bodies. But the peculiar electrical effluvia, which are the most subtile material of diffuse145 humour, entice corpuscles. Air (the common effluvium of the earth) not only unites the disjointed parts, but the earth calls bodies back to itself by means of the intervening air; otherwise bodies which are in higher places would not so eagerly make for the earth. Electrical effluvia differ greatly from air; and as air is the effluvium of the earth, so electricks have their own effluvia and properties, each of them having by reason of its peculiar effluvia a singular tendency toward unity, a motion toward its origin and fount, and toward the body emitting the effluvia. But those substances which by attrition emit a gross or vapourous or aeriform effluvium produce no effect; for either such effluvia are alien to the humour (the uniter of all things), or being very like common air are blended with the air and intermingle with the air, wherefore they produce no effect in the air, and do not cause motions different from those so universal and common in nature. In like manner bodies strive to be united and move on the surface of water, just . as the rod

C, which is put a little way under water. It is plain that the rod E F, which floats on the water by reason of the cork146 H, and only has its wet end F above the surface of the water, is attracted by the rod C, if the rod C is wet a little above the surface of the water; they are suddenly united, just as a drop adjoining a drop is attracted. So a wet thing on the surface of water seeks union with a wet thing, since the surface of the water is raised on both; and they immediately flow together, just like drops or bubbles. But they are in much greater proximity147 than electricks, and are united by their clammy natures. If, however, the whole rod be dry above the water, it no longer attracts, but drives away the stick E F. The same is seen in those bubbles also which are made on water. For we see one drive towards another, and the quicker the nearer they are. Solids are impelled towards solids by the medium of liquid: for example, touch the end of a versorium with the end of a rod on which a drop of water is projecting; as soon as the versorium touches the top of the droplet148, immediately it is joined strongly by a swift motion to the body of the rod. So concreted humid things attract when a little resolved into air (the effluvia in the intermediate space tending to produce unity); for water has on wet bodies, or on bodies wet with abundant moisture on the top of water, the force of an effluvium. Clear air is a convenient medium for an electrical effluvium excited from concreted humour. Wet bodies projecting above the surface of water (if they are near) run together so that they may unite; for the surface of the water is raised around wet substances. But a dry thing is not impelled to a wet one, nor a wet to a dry, but seems to run away. For if all is dry above the water, the surface of the water close to it does not rise, but shuns149 it, the wave sinking around a dry thing. So neither does a wet thing move towards the dry rim22 of a vessel150; but it seeks . a wet rim. A B is the surface of the

water; C D two rods, which stand up wet above the water; it is manifest that the surface of the water is raised at C and D along with the rods; and therefore the rod C, by reason of the water standing up (which seeks its level and unity), moves with the water to D. On E, on the other hand, a wet rod, the water also rises; but on the dry rod F the surface is depressed151; and as it drives to depress also the wave rising on E in its neighbourhood, the higher wave at E turns away from F141; for it does not suffer itself to be depressed. All electrical attraction occurs through an intervening humour; so it is by reason of humour that all things mutually come together; fluids indeed and aqueous bodies on the surface of water, but concreted things, if they have been resolved into vapour, in air; — in air indeed, the effluvium of electricks being very rare, that it may the better permeate152 the medium and not impel119 it by its motion; for if that effluvium had been thick, as that of air, or of the winds, or of saltpetre burnt by fire, as the thick and foul91 effluvia given out with very great force, from other bodies, or air set free from humour by heat rushing out through a pipe (in the instrument of Hero of Alexandria, described in his book Spiritalia), then the effluvium would drive everything away, not allure it. But those rarer effluvia take hold of bodies and embrace them as if with arms extended, with the electricks to which they are united; and they are drawn to the source, the effluvia increasing in strength with the proximity. But what is that effluvium from crystal, glass, and diamond, since these are bodies of considerable hardness and firmly concreted? In order that such an effluvium should be produced, there is no need of any marked or perceptible flux142 of the substance; nor is it necessary that the electrick should be abraded153, or worn away, or deformed. Some odoriferous substances are fragrant154 for many years, exhaling155 continually, yet are not quickly consumed. Cypress wood as long as it is sound, and it lasts a very long time indeed, is redolent; as many learned men attest156 from experience. Such an electrick only for a moment, when stimulated157 by friction, emits powers far more subtile and more fine beyond all odours; yet sometimes amber, jet, sulphur, when they are somewhat easily let free into vapour, also pour out at the same time an odour; and on this account they allure with the very gentlest rubbing, often even without rubbing; they also excite more strongly, and retain hold for a longer time, because they have stronger effluvia and last longer. But diamond, glass, rock-crystal, and numerous others of the harder and firmly concreted gems first grow warm: therefore at first they are rubbed longer, and then they also attract strongly; nor are they otherwise set free into vapour. Everything rushes towards electricks143 excepting flame, and flaming bodies, and the thinnest air. Just as they do not draw flame, in like manner they do not affect a versorium, if on any side it is very near to a flame, either the flame of a lamp or of any burning matter. It is manifest indeed that the effluvia are destroyed by flame and igneous heat; and therefore they attract neither flame nor bodies very near a flame. For electrical effluvia have the virtue of, and are analogous158 with, extenuated159 humour; but they will produce their effect, union and continuity, not by the external impulse of vapours, not by heat and attenuation of heated bodies, but by their humidity itself attenuated into its own peculiar effluvia. Yet they entice smoke sent out by an extinguished light; and the more that smoke is attenuated in seeking the upper regions, the less strongly is it turned aside; for things that are too rarefied are not drawn to them; and at length, when it has now almost vanished, it does not incline towards them at all, which is easily seen against the light. When in fact the smoke has passed into air, it is not moved, as has been demonstrated before. For air itself, if somewhat thin, is not attracted in any way, unless on account of succeeding that which has vacated its place, as in furnaces and such-like, where the air is fed in by mechanical devices for drawing it in. Therefore an effluvium resulting from a non-fouling friction, and one which is not changed by heat, but which is its own, causes union and coherency, a prehension and a congruence towards its source, if only the body to be attracted is not unfitted for motion, either by the surroundings of the bodies or by its own weight. To the bodies therefore of the electricks themselves small bodies are borne. The effluvia extend out their virtue — effluvia which are proper and peculiar to them, and sui generis, differing from common air, being produced from humour, excited by a calorifick motion from attrition and attenuation. And as if they were material rays144, they hold and take up chaff, straws, and twigs, until they become extinct or vanish away: and then they (the corpuscles) being loosed again, attracted by the earth itself, fall down to the earth. The difference between Magneticks and Electricks145 is that all magneticks run together with mutual65 forces; electricks only allure; that which is allured is not changed by an implanted force, but that which has moved up to them voluntarily rests upon them by the law of matter. Bodies are borne towards electricks in a straight line towards the centre of the electrick; a loadstone draws a loadstone directly at the poles only, in other parts obliquely160 and transversely, and in this way also they adhere and hang to one another. Electrical motion is a motion of aggregation161 of matter; magnetical motion is one of disposition162 and conformation. The globe of the earth is aggregated163 and cohæres by itself electrically. The globe of the earth is directed and turned magnetically; at the same time also it both cohæres, and in order that it may be solid, is in its inmost parts cemented together.

点击 收听单词发音
收听单词发音
 收听单词发音
收听单词发音
1
amber

|
|
| n.琥珀;琥珀色;adj.琥珀制的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
2
memoirs

|
|
| n.回忆录;回忆录传( mem,自oir的名词复数) | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
3
invoke

|
|
| v.求助于(神、法律);恳求,乞求 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
4
inquisitive

|
|
| adj.求知欲强的,好奇的,好寻根究底的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
5
purgative

|
|
| n.泻药;adj.通便的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
6
likeness

|
|
| n.相像,相似(之处) | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
7
err

|
|
| vi.犯错误,出差错 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
8
conspicuous

|
|
| adj.明眼的,惹人注目的;炫耀的,摆阔气的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
9
remarkable

|
|
| adj.显著的,异常的,非凡的,值得注意的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
10
inclination

|
|
| n.倾斜;点头;弯腰;斜坡;倾度;倾向;爱好 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
11
moors

|
|
| v.停泊,系泊(船只)( moor的第三人称单数 ) | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
12
chaff

|
|
| v.取笑,嘲笑;n.谷壳 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
13
rustics

|
|
| n.有农村或村民特色的( rustic的名词复数 );粗野的;不雅的;用粗糙的木材或树枝制作的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
14
bitumen

|
|
| n.沥青 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
15
viscous

|
|
| adj.粘滞的,粘性的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
16
gnats

|
|
| n.叮人小虫( gnat的名词复数 ) | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
17
forth

|
|
| adv.向前;向外,往外 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
18
transformation

|
|
| n.变化;改造;转变 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
19
crammed

|
|
| adj.塞满的,挤满的;大口地吃;快速贪婪地吃v.把…塞满;填入;临时抱佛脚( cram的过去式) | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
20
abstruse

|
|
| adj.深奥的,难解的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
21
enticing

|
|
| adj.迷人的;诱人的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
22
rim

|
|
| n.(圆物的)边,轮缘;边界 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
23
cryptic

|
|
| adj.秘密的,神秘的,含义模糊的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
24
akin

|
|
| adj.同族的,类似的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
25
investigation

|
|
| n.调查,调查研究 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
26
inert

|
|
| adj.无活动能力的,惰性的;迟钝的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
27
uncommon

|
|
| adj.罕见的,非凡的,不平常的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
28
entice

|
|
| v.诱骗,引诱,怂恿 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
29
sapphire

|
|
| n.青玉,蓝宝石;adj.天蓝色的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
30
iris

|
|
| n.虹膜,彩虹 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
31
gem

|
|
| n.宝石,珠宝;受爱戴的人 [同]jewel | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
32
amethyst

|
|
| n.紫水晶 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
33
possessed

|
|
| adj.疯狂的;拥有的,占有的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
34
lucid

|
|
| adj.明白易懂的,清晰的,头脑清楚的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
35
gems

|
|
| growth; economy; management; and customer satisfaction 增长 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
36
resin

|
|
| n.树脂,松香,树脂制品;vt.涂树脂 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
37
entices

|
|
| 诱惑,怂恿( entice的第三人称单数 ) | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
38
twigs

|
|
| 细枝,嫩枝( twig的名词复数 ) | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
39
inexplicable

|
|
| adj.无法解释的,难理解的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
40
utterly

|
|
| adv.完全地,绝对地 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
41
digits

|
|
| n.数字( digit的名词复数 );手指,足趾 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
42
thereby

|
|
| adv.因此,从而 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
43
unctuous

|
|
| adj.油腔滑调的,大胆的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
44
fully

|
|
| adv.完全地,全部地,彻底地;充分地 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
45
derive

|
|
| v.取得;导出;引申;来自;源自;出自 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
46
virtue

|
|
| n.德行,美德;贞操;优点;功效,效力 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
47
derived

|
|
| vi.起源;由来;衍生;导出v.得到( derive的过去式和过去分词 );(从…中)得到获得;源于;(从…中)提取 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
48
allure

|
|
| n.诱惑力,魅力;vt.诱惑,引诱,吸引 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
49
tepid

|
|
| adj.微温的,温热的,不太热心的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
50
previously

|
|
| adv.以前,先前(地) | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
51
imbibe

|
|
| v.喝,饮;吸入,吸收 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
52
variance

|
|
| n.矛盾,不同 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
53
provender

|
|
| n.刍草;秣料 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
54
diminution

|
|
| n.减少;变小 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
55
devoured

|
|
| 吞没( devour的过去式和过去分词 ); 耗尽; 津津有味地看; 狼吞虎咽地吃光 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
56
friction

|
|
| n.摩擦,摩擦力 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
57
exhausted

|
|
| adj.极其疲惫的,精疲力尽的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
58
incandescent

|
|
| adj.遇热发光的, 白炽的,感情强烈的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
59
imputed

|
|
| v.把(错误等)归咎于( impute的过去式和过去分词 ) | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
60
resounding

|
|
| adj. 响亮的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
61
accredited

|
|
| adj.可接受的;可信任的;公认的;质量合格的v.相信( accredit的过去式和过去分词 );委托;委任;把…归结于 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
62
allured

|
|
| 诱引,吸引( allure的过去式和过去分词 ) | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
63
cogent

|
|
| adj.强有力的,有说服力的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
64
drawn

|
|
| v.拖,拉,拔出;adj.憔悴的,紧张的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
65
mutual

|
|
| adj.相互的,彼此的;共同的,共有的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
66
potency

|
|
| n. 效力,潜能 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
67
aglow

|
|
| adj.发亮的;发红的;adv.发亮地 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
68
purging

|
|
| 清洗; 清除; 净化; 洗炉 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
69
morbid

|
|
| adj.病的;致病的;病态的;可怕的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
70
purgatives

|
|
| 泻剂( purgative的名词复数 ) | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
|
71
fermenting

|
|
| v.(使)发酵( ferment的现在分词 );(使)激动;骚动;骚扰 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
72
imbibes

|
|
| v.吸收( imbibe的第三人称单数 );喝;吸取;吸气 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
73
tusks

|
|
| n.(象等动物的)长牙( tusk的名词复数 );獠牙;尖形物;尖头 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
74
allures

|
|
| 诱引,吸引( allure的第三人称单数 ) | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
75
agate

|
|
| n.玛瑙 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
76
alabaster

|
|
| adj.雪白的;n.雪花石膏;条纹大理石 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
77
cedar

|
|
| n.雪松,香柏(木) | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
78
cypress

|
|
| n.柏树 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
79
brass

|
|
| n.黄铜;黄铜器,铜管乐器 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
80
consistency

|
|
| n.一贯性,前后一致,稳定性;(液体的)浓度 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
81
sufficiently

|
|
| adv.足够地,充分地 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
82
dross

|
|
| n.渣滓;无用之物 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
83
mica

|
|
| n.云母 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
84
primordial

|
|
| adj.原始的;最初的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
85
exhaled

|
|
| v.呼出,发散出( exhale的过去式和过去分词 );吐出(肺中的空气、烟等),呼气 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
86
exhale

|
|
| v.呼气,散出,吐出,蒸发 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
87
degradation

|
|
| n.降级;低落;退化;陵削;降解;衰变 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
88
deformed

|
|
| adj.畸形的;变形的;丑的,破相了的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
89
remains

|
|
| n.剩余物,残留物;遗体,遗迹 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
90
watery

|
|
| adj.有水的,水汪汪的;湿的,湿润的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
91
foul

|
|
| adj.污秽的;邪恶的;v.弄脏;妨害;犯规;n.犯规 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
92
fouled

|
|
| v.使污秽( foul的过去式和过去分词 );弄脏;击球出界;(通常用废物)弄脏 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
93
plentiful

|
|
| adj.富裕的,丰富的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
94
mingled

|
|
| 混合,混入( mingle的过去式和过去分词 ); 混进,与…交往[联系] | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
95
solicit

|
|
| vi.勾引;乞求;vt.请求,乞求;招揽(生意) | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
96
peculiar

|
|
| adj.古怪的,异常的;特殊的,特有的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
97
virtues

|
|
| 美德( virtue的名词复数 ); 德行; 优点; 长处 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
98
ignoble

|
|
| adj.不光彩的,卑鄙的;可耻的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
99
linen

|
|
| n.亚麻布,亚麻线,亚麻制品;adj.亚麻布制的,亚麻的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
100
suffused

|
|
| v.(指颜色、水气等)弥漫于,布满( suffuse的过去式和过去分词 ) | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
101
planks

|
|
| (厚)木板( plank的名词复数 ); 政纲条目,政策要点 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
102
slabs

|
|
| n.厚板,平板,厚片( slab的名词复数 );厚胶片 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
103
barley

|
|
| n.大麦,大麦粒 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
104
enveloped

|
|
| v.包围,笼罩,包住( envelop的过去式和过去分词 ) | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
105
igneous

|
|
| adj.火的,火绒的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
106
vigour

|
|
| (=vigor)n.智力,体力,精力 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
107
corrupts

|
|
| (使)败坏( corrupt的第三人称单数 ); (使)腐化; 引起(计算机文件等的)错误; 破坏 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
108
innate

|
|
| adj.天生的,固有的,天赋的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
109
circumference

|
|
| n.圆周,周长,圆周线 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
110
cleansed

|
|
| 弄干净,清洗( cleanse的过去式和过去分词 ) | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
111
extraneous

|
|
| adj.体外的;外来的;外部的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
112
copiously

|
|
| adv.丰富地,充裕地 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
113
herd

|
|
| n.兽群,牧群;vt.使集中,把…赶在一起 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
114
denser

|
|
| adj. 不易看透的, 密集的, 浓厚的, 愚钝的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
115
ascend

|
|
| vi.渐渐上升,升高;vt.攀登,登上 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
116
attenuated

|
|
| v.(使)变细( attenuate的过去式和过去分词 );(使)变薄;(使)变小;减弱 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
117
attenuating

|
|
| v.(使)变细( attenuate的现在分词 );(使)变薄;(使)变小;减弱 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
118
impelled

|
|
| v.推动、推进或敦促某人做某事( impel的过去式和过去分词 ) | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
119
impel

|
|
| v.推动;激励,迫使 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
120
penetrate

|
|
| v.透(渗)入;刺入,刺穿;洞察,了解 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
121
applied

|
|
| adj.应用的;v.应用,适用 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
122
prone

|
|
| adj.(to)易于…的,很可能…的;俯卧的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
123
downwards

|
|
| adj./adv.向下的(地),下行的(地) | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
124
apprehension

|
|
| n.理解,领悟;逮捕,拘捕;忧虑 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
125
momentary

|
|
| adj.片刻的,瞬息的;短暂的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
126
attenuation

|
|
| n.变薄;弄细;稀薄化;减少 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
127
spherical

|
|
| adj.球形的;球面的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
128
standing

|
|
| n.持续,地位;adj.永久的,不动的,直立的,不流动的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
129
cone

|
|
| n.圆锥体,圆锥形东西,球果 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
130
skilfully

|
|
| adv. (美skillfully)熟练地 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
131
repelled

|
|
| v.击退( repel的过去式和过去分词 );使厌恶;排斥;推开 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
132
exhales

|
|
| v.呼出,发散出( exhale的第三人称单数 );吐出(肺中的空气、烟等),呼气 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
133
evoked

|
|
| [医]诱发的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
134
diffusion

|
|
| n.流布;普及;散漫 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
135
lighter

|
|
| n.打火机,点火器;驳船;v.用驳船运送;light的比较级 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
136
stifled

|
|
| (使)窒息, (使)窒闷( stifle的过去式和过去分词 ); 镇压,遏制; 堵 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
137
affected

|
|
| adj.不自然的,假装的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
138
entirely

|
|
| ad.全部地,完整地;完全地,彻底地 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
139
obstruct

|
|
| v.阻隔,阻塞(道路、通道等);n.阻碍物,障碍物 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
140
proceeding

|
|
| n.行动,进行,(pl.)会议录,学报 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
141
radius

|
|
| n.半径,半径范围;有效航程,范围,界限 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
142
unity

|
|
| n.团结,联合,统一;和睦,协调 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
143
participation

|
|
| n.参与,参加,分享 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
144
incitement

|
|
| 激励; 刺激; 煽动; 激励物 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
145
diffuse

|
|
| v.扩散;传播;adj.冗长的;四散的,弥漫的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
146
cork

|
|
| n.软木,软木塞 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
147
proximity

|
|
| n.接近,邻近 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
148
droplet

|
|
| n.小滴,飞沫 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
149
shuns

|
|
| v.避开,回避,避免( shun的第三人称单数 ) | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
150
vessel

|
|
| n.船舶;容器,器皿;管,导管,血管 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
151
depressed

|
|
| adj.沮丧的,抑郁的,不景气的,萧条的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
152
permeate

|
|
| v.弥漫,遍布,散布;渗入,渗透 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
153
abraded

|
|
| adj.[医]刮擦的v.刮擦( abrade的过去式和过去分词 );(在精神方面)折磨(人);消磨(意志、精神等);使精疲力尽 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
154
fragrant

|
|
| adj.芬香的,馥郁的,愉快的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
155
exhaling

|
|
| v.呼出,发散出( exhale的现在分词 );吐出(肺中的空气、烟等),呼气 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
156
attest

|
|
| vt.证明,证实;表明 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
157
stimulated

|
|
| a.刺激的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
158
analogous

|
|
| adj.相似的;类似的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
159
extenuated

|
|
| v.(用偏袒的辩解或借口)减轻( extenuate的过去式和过去分词 );低估,藐视 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
160
obliquely

|
|
| adv.斜; 倾斜; 间接; 不光明正大 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
161
aggregation

|
|
| n.聚合,组合;凝聚 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
162
disposition

|
|
| n.性情,性格;意向,倾向;排列,部署 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
163
aggregated

|
|
| a.聚合的,合计的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
| 欢迎访问英文小说网 |

