At first, in all probability, the normal course of pre-historic man was followed—wheat and barley grew wild, were first eaten raw, and then parched4. Of this latter and primitive5 method of cooking cereals we have several notices. It was used as a sacrifice, as we see in Leviticus ii. 16: ‘And the priest shall burn the memorial of it, part of the beaten corn thereof, and part of the oil thereof, with all the frankincense thereof: it is an offering made by fire unto the Lord.’ That parched corn was at that time a food we find in Levit. xxiii. 14: ‘And ye shall eat neither bread, nor parched corn, nor green ears, until the self-same day that ye have brought an offering unto your God.’ We next find it as the food of labouring30 people in Ruth ii. 14, when Boaz ‘reached her parched corn, and she did eat, and was sufficed, and left.’
Mention is again made of it in I. Sam. xvii., when Goliath of Gath challenged the men of Israel. Jesse’s three sons had followed Saul to the battle, and the anxious father had sent his youngest son David, with provisions for them, and a present to their commander, vv. 17, 18: ‘And Jesse said unto David his son, Take now for thy brethren an ephah4 of this parched corn, and these ten loaves, and run to the camp to thy brethren; and carry these ten cheeses unto the captain of their thousand, and look how thy brethren fare, and take their pledge.’ We see, I. Sam. xxv. 18, how Abigail, Nabal’s wife, in order to propitiate6 David, ‘made haste, and took 200 loaves, and two bottles of wine, and five sheep ready dressed, and five measures of parched corn, and 100 clusters of raisins7, and 200 cakes of figs8, and laid them on asses9.’ The last we hear of parched corn as food is in II. Sam. xvii. 27, 28, when David arrived at Mahanaim. Shobi, Machir, and Barzillai ‘brought beds, and basons, and earthen vessels10, and wheat, and barley, and flour, and parched corn, and beans, and lentils, and parched pulse.’ In England this parching11 is sometimes applied12 to peas, and, indeed, there is a saying comparing an extremely lively person ‘to a parched pea in a frying pan,’ and in America ‘pop corn,’ or parched maize13, is very popular.
Threshing corn we first read of in Deut. xxv. 4, when we find the following direction given: ‘Thou shalt not muzzle14 the ox when he treadeth out the 31corn,’ a practice which the natives of Aleppo, and some other Eastern places, still religiously observe.
How Gideon (Jud. vi. 11) or Oman (I. Chron. xxi. 20) threshed, whether by oxen or by flail15, we cannot tell, but in Isaiah xxviii. 27, 28, we find five methods of threshing then in vogue16. ‘For the fitches [this is supposed to be the Nigella sativa, whose seeds are used as a condiment17, like coriander or caraway] are not threshed with a threshing instrument, neither is a cart wheel turned about upon the cummin; but the fitches are beaten out with a staff, and the cummin with a rod. Bread corn is bruised18; because he will not ever be threshing it, nor break it with the wheel of his cart, nor bruise19 it with his horsemen.’ In Lowth on Isaiah we find this passage made somewhat clearer:
‘The dill is not beaten out with the corn-drag;
Nor is the Wheel of the Wain made to turn upon the cummin.
But the dill is beaten out with the Staff,
And the cummin with the Flail, but
The bread corn with the Threshing-Wain;
And not for ever will he continue thus to thresh it,
Nor vex20 it with the Wheel of its Wain,
Nor to bruise it with the Hoofs21 of his Cattle.’
The Staff and Flail were used for that grain that was too tender to be treated in any other method. The Drag consisted of a sort of frame of strong planks23, made rough at the bottom with hard stones or iron; it was drawn24 by horses or oxen over the corn sheaves spread on the threshing floor, the driver sitting upon it. The Wain was much like the former,32 but had wheels with iron teeth, or edges like a saw; the axle was armed with iron teeth or serrated wheels throughout; it moved upon three rollers, armed with iron teeth, or wheels, to cut the straw. In Syria they make use of the drag constructed in the very same manner—and this not only forces out the grain, but cuts the straw in pieces for fodder25 for the cattle; for in Eastern countries there is no hay.
Sir R. K. Porter, in his Travels in Georgia,5 speaks of this method of threshing, which he saw in the early part of the last century. ‘The threshing operation is managed by a machine composed of a large square frame of wood, which contains two wooden cylinders26 placed parallel to each other, and which have a turning motion. They are stuck full of splinters, with sharp square points, but not all of a length. These barrels have the appearance of the barrels in an organ, and their projections27, when brought in contact with the corn, break the stalk and disengage the ear. They are put in motion by a couple of cows or oxen, yoked28 to the frame, and guided by a man sitting on the plank22 that covers the frame which contains the cylinders. He drives this agricultural equipage in a circle round any great accumulation of just-gathered harvest, keeping at a certain distance from the verge29 of the heap, close to which a second peasant stands, holding a long-handled 20-pronged fork, shaped like the spread sticks of a fan, and with which he throws the unbound sheaves forward to meet the rotary30 motion of the machine. He has a shovel31 also ready, with which he removes to 33a considerable distance the corn that has already passed the wheel. Other men are on the spot with the like implement32, which they fill with the broken material, and throw it aloft in the air, where the wind blows away the chaff33, and the grain falls to the ground. The latter process is repeated till the corn is completely winnowed34 from its refuse, when it is gathered up, carried home, and deposited for use in large earthen jars. The straw is preserved with care, being the sole winter food of the horses and mules35. But while I looked on at the patriarchal style of husbandry, and at the strong yet docile36 animal, which for so many ages had been the right hand of man in his business of tilling and reaping the ground, I could not but revere37 the beneficent law which pronounced, “Muzzle not the ox when he treadeth out the corn.”’
It was probably one of these that Araunah meant (II. Sam. xxiv. 22) when he said unto David: ‘Let my lord the king take and offer up what seemeth good unto him: behold38, here be oxen for burnt sacrifice, and threshing instruments and other instruments of the oxen for wood.’ And it is certainly mentioned in Isaiah xli. 15: ‘Behold, I will make thee a new sharp threshing instrument having teeth.’
The threshing-floor is many times mentioned in the Bible. There were those of Atad, Nachon, and Araunah (or Ornan), the value of whose floor, etc., is variously stated in II. Sam. xxiv. 24, where it says that David bought the flour and oxen for 50 shekels of silver, or about 6l of our money; whilst in I. Chron. xxi. 25, he gave him 600 shekels of gold in weight, or 1200l of our currency, which seems a34 large sum for a small level piece of ground; for the floors, so-called, were out of doors, so that the wind might carry away the chaff, as we read in Hosea xiii. 3: ‘They shall be ... as the chaff that is driven with the whirlwind out of the floor.’ See also Psalm39 i. 4.
These floors were used for other purposes than threshings, as we read in I. Kings xxii. 10: ‘And the king of Israel and Jehoshaphat the king of Judah sat each on his throne, having put on their robes, in a void place (or floor) in the entrance of the gate of Samaria; and all the prophets prophesied40 before them,’ a statement which is repeated in II. Chron. xviii. 9.
Harvest-time was appointed by Moses as one of the great festivals—Exodus41 xxiii. 14, etc.: ‘Three times thou shalt keep a feast unto me in the year. Thou shalt keep the feast of unleavened bread: (thou shalt eat unleavened bread seven days, as I commanded thee, in the time appointed of the month Abib; for in it thou camest out from Egypt: and none shall appear before me empty). And the feast of harvest, the first-fruits of thy labours, which thou hast sown in the field: and the feast of ingathering, which is in the end of the year, when thou hast gathered in thy labours out of the field.’ And again, in Exodus xxxiv., this is repeated, with the addition (v. 21): ‘Six days thou shalt work, but on the seventh day thou shalt rest: in earing time and in harvest thou shalt rest.’ This holiday was, and is, called the feast of tabernacles, and we read in Deut. xvi. 13, etc.: ‘Thou shalt observe the feast of tabernacles seven35 days, after that thou hast gathered in thy corn and thy wine: and thou shalt rejoice in thy feast, thou, and thy son, and thy daughter, and thy man-servant, and thy maid-servant, and the Levite, the stranger, and the fatherless, and the widow, that are within thy gates. Seven days shalt thou keep a solemn feast unto the Lord thy God in the place which the Lord shall choose: because the Lord thy God shall bless thee in all thine increase, and in all the works of thine hands, therefore thou shalt surely rejoice.’
In the story of Ruth we get an idyllic44 picture of a Hebrew harvest field, with its kindly45 greetings between master and man, and its gleaners. Naomi, a native of Bethlehem, returned thither47 from Moab, after the death of her husband, Elimelech, accompanied by her daughter-in-law Ruth, who was also a widow, ‘and they came to Bethlehem in the beginning of barley harvest.’
Special favour was accorded to Ruth. She might glean46 ‘among the sheaves’—i.e., following the reapers48, instead of waiting until the corn had been carried; but the Jews were enjoined49 to be liberal in the matter of gleaning50, as we see by Lev. xix. 9: ‘And when ye reap the harvest of your land, thou shalt not wholly reap the corners of thy field, neither shalt thou gather the gleanings of thy harvest’; and in Deut. xxiv. 19, ‘When thou cuttest down thine harvest in thy field, and hast forgot a sheaf in the field, thou shalt not go again to fetch it; it shall be for the stranger, for the fatherless, and for the widow: that the Lord thy God may bless thee in all the work of thine hands.’
There were no public mills at which flour could be36 ground, but, as now, in the unchangeable East, every family ground their own corn, and this task, as well as the making and baking of bread, was left to the women. See Matt. xxiv. 41: ‘Two women shall be grinding at the mill; the one shall be taken, and the other left.’ Again we find that it was a woman who was grinding corn on a housetop in Thebez who (Judges ix. 53) ‘cast a piece of a millstone upon Abimelech’s head, and all to brake his skull51.’ An Eastern flour mill consists of two stones, the upper one rotating on the lower. In Shaw’s Travels, p. 297, he says: ‘Most families grind their wheat and barley at home, having two portable millstones for that purpose. The uppermost is turned round by a small handle of wood or iron placed in the edge of it. When this stone is large, or expedition is required, then a second person is called in to assist. It is usual for the women alone to be concerned in this employ, setting themselves down over against each other, with the millstones between them.’
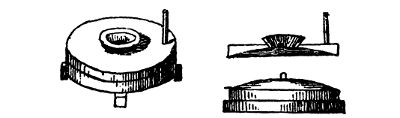
A Palestine Hand-mill.
And Dr. Clarke, in his Travels,6 says, that at Nazareth: ‘Scarcely had we reached the apartment prepared for our reception, when, looking into the 37courtyard belonging to the house, we beheld52 two women grinding at the mill in a manner most forcibly illustrating53 the saying of our Saviour54. They were preparing flour to make our bread, as it is always customary in the country when strangers arrive. The two women, seated upon the ground opposite to each other, held between them two round, flat stones, such as are seen in Lapland, and such as in Scotland are called querns. In the centre of the upper stone was a cavity for pouring in the corn, and by the side of this an upright wooden handle for moving the stone. As the operation began, one of the women with her right hand pushed this handle to the woman opposite, who again sent it to her companion, thus communicating a rotary and very rapid motion to the upper stone, their left hands being all the while employed in supplying fresh corn as fast as the bran and flour escaped from the sides of the machine.’
Of such importance among the household treasures of the Hebrews was the flour mill esteemed55 that Moses laid it down (Deut. xxiv. 6): ‘No man shall take the nether56 or the upper millstone to pledge: for he taketh a man’s life to pledge.’
The first mention of bread in the Bible, with the exception of Adam’s curse, is in Gen. xiv. 18: ‘And Melchizedek, King of Salem, brought forth57 bread and wine’; but it is pre-supposed, in Chap. xii. 10: ‘And there was a famine in the land: and Abram went down into Egypt to sojourn58 there; for the famine was grievous in the land.’ When the three angels visited him on the plains of Mamre, he offered them hospitality (Gen. xviii. 5, 6): ‘I will fetch a morsel38 of bread, and comfort ye your hearts; after that ye shall pass on: for therefore are ye come to your servant. And they said, So do, as thou hast said. And Abraham hastened into the tent unto Sarah, and said, Make ready quickly three measures of fine meal, knead it, and make cakes upon the hearth59.’ And to this day in Syria cakes are made upon the hearth, and the breaking of bread together is a token of amity60 and protection extended by the stronger to the weaker.
Of what shape the Hebrew bread was we do not know, for no representation of it has come down to us. As a rule it was possibly in the form of thin flat round cakes—similar to those unleavened biscuits now used by the Jews during their Passover, and the form and dimensions of which are probably traditional—but they also had loaves of bread, as we read in many places. The Shew, or Presence bread, must have been loaves, because of the quantity of flour in each—between five and six pints61. The directions for making it, etc., are plain enough (Lev. xxiv. 5-9): ‘And thou shalt take fine flour, and bake twelve cakes thereof: two tenth deals shall be in one cake. And thou shalt set them in two rows, six on a row, upon the pure table before the Lord. And thou shalt put pure frankincense upon each row, that it may be on the bread for a memorial, even an offering made by fire unto the Lord. Every Sabbath he shall set it in order before the Lord continually, being taken from the children of Israel by an everlasting62 covenant63. And it shall be Aaron’s and his sons’; and they shall eat it in the holy place: for it is most holy unto him39 of the offerings of the Lord made by fire by a perpetual statute64.’
This shew bread must have been leavened43, for a cake containing nearly three quarts of flour, and unleavened, could hardly be. We have no certainty as to the shape of these twelve loaves, typical of the tribes of Israel; for, although the gold table on which it was placed figures in a bas relief on the Arch of Titus at Rome, there is no bread upon it. The Rabbis say that the loaves were square, and covered with leaves of gold; and that they were placed in two piles of six each, one upon another, on the opposite ends of the table; and that between every two loaves were laid three semi-tubes, like slit65 canes66, of gold, for the purpose of keeping the cakes the better from mouldiness and corruption67 by admitting the air between them; and it is also said, but upon what authority I know not, that each end of the table was furnished with a tall, three-pronged fork of gold, one at each corner, standing68 perpendicularly69, for the purpose of keeping the loaves in their proper places.
The new bread was set on the table with much ceremony every Sabbath, and it was so ordered that the new bread should be set on one end of the table before the old was taken away from the other, in order that the table might not be for a moment without bread. Jewish tradition states that, to render the bread more peculiar70 and consecrated71 from its origin, the priests themselves performed all the operations of sowing, reaping and grinding the corn for the shew bread, as well as of kneading and baking the bread itself. On the table was, probably, some40 salt, as we read in Lev. ii. 13: ‘With all thine offerings thou shalt offer salt.’
There seems to be little doubt but that the Israelites knew nothing about leavened bread until they went into Egypt, and that they obtained that knowledge from the civilised Egyptians. That they did leaven42 their bread we learn from Exodus xii. 34-39: ‘And the people took their dough72 before it was leavened, their kneading-troughs being bound up in their clothes upon their shoulders.... And they baked unleavened cakes of the dough which they brought forth out of Egypt, for it was not leavened; because they were thrust out of Egypt, and could not tarry, neither had they prepared for themselves any victual.’
Bread was sometimes dipped in oil as a relish73, and in this state it was also used in sacrifice. Lev. viii. 26: ‘And out of the basket of unleavened bread, that was before the Lord, he took one unleavened cake, and a cake of oiled bread, and one wafer,’ etc.; and, occasionally, as we see in Ruth, it was dipped in vinegar. The Jew thanked God for all His good gifts, and with his bread, he took it in his hands, and pronounced the following benediction74: ‘Blessed art Thou, O Lord our God, the King of the world, that produceth bread out of the earth.’ If there were many at table, one asked a blessing75 for the rest. The blessing always preceded the breaking of the bread. The rules concerning the breaking of bread were—the master of the house recited and finished the blessing, and after that he broke the bread; he did not break a small piece, lest he should seem to be41 sparing; nor a large piece, lest he should be thought to be famished76; it was a principal command to break a whole loaf. He that broke the bread put a piece before everyone, and the other took it into his hand. The master of the family ate first of the bread after blessing. Maimonides, writing on Halacoth, or legal formul? (Beracoth, c. 7), says the guests were not to eat or taste anything till he who broke had tasted first, nor was it permitted at festivals for any of the guests to drink of the cup till the master of the family had done so.
There are several unleavened bread bakeries in London, and one each in Birmingham and Leeds, to supply the Jews resident in the neighbourhood with Passover cakes, or Matzos. Of course, there is an enormous demand for this sort of unleavened bread, and to meet it these bakeries begin baking two months before the commencement of the Passover. These Matzos look like ordinary large water biscuits, except that they are a foot or more in diameter. They are made of flour and water, and contain no other ingredient.
After the flour has been kneaded into a very stiff dough, a lump of it, weighing about 50 lb., is placed on a great block of wood and pressed into a thick sheet by a heavy beam, which is fastened to the block at one end by an iron link and staple77. This sheet is next placed under an iron roller, from which it emerges in a long ribbon. It passes under another roller, and another, and then it is thin enough for baking. It is now stamped and cut into the unbaked Matzos, which are placed upon a large peel, or wooden42 tray, having a long handle, and deposited in an oven. Three minutes later they are taken out, white, but crisp. From the oven they are conveyed to the packing room, where they are allowed to cool, after which they are put up in stacks, and thus kept ready for delivery. Of course, during the whole of Passover week the Jews eat no other bread.

点击 收听单词发音
收听单词发音
 收听单词发音
收听单词发音
1
barley

|
|
| n.大麦,大麦粒 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
2
millet

|
|
| n.小米,谷子 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
3
accurately

|
|
| adv.准确地,精确地 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
4
parched

|
|
| adj.焦干的;极渴的;v.(使)焦干 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
5
primitive

|
|
| adj.原始的;简单的;n.原(始)人,原始事物 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
6
propitiate

|
|
| v.慰解,劝解 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
7
raisins

|
|
| n.葡萄干( raisin的名词复数 ) | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
8
figs

|
|
| figures 数字,图形,外形 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
9
asses

|
|
| n. 驴,愚蠢的人,臀部 adv. (常用作后置)用于贬损或骂人 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
10
vessels

|
|
| n.血管( vessel的名词复数 );船;容器;(具有特殊品质或接受特殊品质的)人 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
11
parching

|
|
| adj.烘烤似的,焦干似的v.(使)焦干, (使)干透( parch的现在分词 );使(某人)极口渴 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
12
applied

|
|
| adj.应用的;v.应用,适用 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
13
maize

|
|
| n.玉米 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
14
muzzle

|
|
| n.鼻口部;口套;枪(炮)口;vt.使缄默 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
15
flail

|
|
| v.用连枷打;击打;n.连枷(脱粒用的工具) | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
16
Vogue

|
|
| n.时髦,时尚;adj.流行的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
17
condiment

|
|
| n.调味品 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
18
bruised

|
|
| [医]青肿的,瘀紫的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
19
bruise

|
|
| n.青肿,挫伤;伤痕;vt.打青;挫伤 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
20
vex

|
|
| vt.使烦恼,使苦恼 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
21
hoofs

|
|
| n.(兽的)蹄,马蹄( hoof的名词复数 )v.(兽的)蹄,马蹄( hoof的第三人称单数 ) | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
22
plank

|
|
| n.板条,木板,政策要点,政纲条目 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
23
planks

|
|
| (厚)木板( plank的名词复数 ); 政纲条目,政策要点 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
24
drawn

|
|
| v.拖,拉,拔出;adj.憔悴的,紧张的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
25
fodder

|
|
| n.草料;炮灰 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
26
cylinders

|
|
| n.圆筒( cylinder的名词复数 );圆柱;汽缸;(尤指用作容器的)圆筒状物 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
27
projections

|
|
| 预测( projection的名词复数 ); 投影; 投掷; 突起物 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
28
yoked

|
|
| 结合(yoke的过去式形式) | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
29
verge

|
|
| n.边,边缘;v.接近,濒临 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
30
rotary

|
|
| adj.(运动等)旋转的;轮转的;转动的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
31
shovel

|
|
| n.铁锨,铲子,一铲之量;v.铲,铲出 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
32
implement

|
|
| n.(pl.)工具,器具;vt.实行,实施,执行 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
33
chaff

|
|
| v.取笑,嘲笑;n.谷壳 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
34
winnowed

|
|
| adj.扬净的,风选的v.扬( winnow的过去式和过去分词 );辨别;选择;除去 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
35
mules

|
|
| 骡( mule的名词复数 ); 拖鞋; 顽固的人; 越境运毒者 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
36
docile

|
|
| adj.驯服的,易控制的,容易教的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
37
revere

|
|
| vt.尊崇,崇敬,敬畏 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
38
behold

|
|
| v.看,注视,看到 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
39
psalm

|
|
| n.赞美诗,圣诗 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
40
prophesied

|
|
| v.预告,预言( prophesy的过去式和过去分词 ) | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
41
exodus

|
|
| v.大批离去,成群外出 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
42
leaven

|
|
| v.使发酵;n.酵母;影响 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
43
leavened

|
|
| adj.加酵母的v.使(面团)发酵( leaven的过去式和过去分词 );在…中掺入改变的因素 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
44
idyllic

|
|
| adj.质朴宜人的,田园风光的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
45
kindly

|
|
| adj.和蔼的,温和的,爽快的;adv.温和地,亲切地 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
46
glean

|
|
| v.收集(消息、资料、情报等) | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
47
thither

|
|
| adv.向那里;adj.在那边的,对岸的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
48
reapers

|
|
| n.收割者,收获者( reaper的名词复数 );收割机 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
49
enjoined

|
|
| v.命令( enjoin的过去式和过去分词 ) | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
50
gleaning

|
|
| n.拾落穗,拾遗,落穗v.一点点地收集(资料、事实)( glean的现在分词 );(收割后)拾穗 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
51
skull

|
|
| n.头骨;颅骨 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
52
beheld

|
|
| v.看,注视( behold的过去式和过去分词 );瞧;看呀;(叙述中用于引出某人意外的出现)哎哟 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
53
illustrating

|
|
| 给…加插图( illustrate的现在分词 ); 说明; 表明; (用示例、图画等)说明 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
54
saviour

|
|
| n.拯救者,救星 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
55
esteemed

|
|
| adj.受人尊敬的v.尊敬( esteem的过去式和过去分词 );敬重;认为;以为 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
56
nether

|
|
| adj.下部的,下面的;n.阴间;下层社会 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
57
forth

|
|
| adv.向前;向外,往外 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
58
sojourn

|
|
| v./n.旅居,寄居;逗留 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
59
hearth

|
|
| n.壁炉炉床,壁炉地面 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
60
amity

|
|
| n.友好关系 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
61
pints

|
|
| n.品脱( pint的名词复数 );一品脱啤酒 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
62
everlasting

|
|
| adj.永恒的,持久的,无止境的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
63
covenant

|
|
| n.盟约,契约;v.订盟约 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
64
statute

|
|
| n.成文法,法令,法规;章程,规则,条例 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
65
slit

|
|
| n.狭长的切口;裂缝;vt.切开,撕裂 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
66
canes

|
|
| n.(某些植物,如竹或甘蔗的)茎( cane的名词复数 );(用于制作家具等的)竹竿;竹杖 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
67
corruption

|
|
| n.腐败,堕落,贪污 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
68
standing

|
|
| n.持续,地位;adj.永久的,不动的,直立的,不流动的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
69
perpendicularly

|
|
| adv. 垂直地, 笔直地, 纵向地 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
70
peculiar

|
|
| adj.古怪的,异常的;特殊的,特有的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
71
consecrated

|
|
| adj.神圣的,被视为神圣的v.把…奉为神圣,给…祝圣( consecrate的过去式和过去分词 );奉献 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
72
dough

|
|
| n.生面团;钱,现款 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
73
relish

|
|
| n.滋味,享受,爱好,调味品;vt.加调味料,享受,品味;vi.有滋味 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
74
benediction

|
|
| n.祝福;恩赐 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
75
blessing

|
|
| n.祈神赐福;祷告;祝福,祝愿 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
76
famished

|
|
| adj.饥饿的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
77
staple

|
|
| n.主要产物,常用品,主要要素,原料,订书钉,钩环;adj.主要的,重要的;vt.分类 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
| 欢迎访问英文小说网 |

