The Difference between Historic and Prehistoric Time.
It will be necessary before we examine the group of caves used by man in prehistoric times, to point out the important difference in the measurement of time within and beyond the borders of history. When we speak, for example, of the date of the Norman Conquest, we imply that we can ascertain3 by historical records, not merely that it succeeded the invasion of Britain by the English or Danes, and happened before our own time, but that the interval4 which separates it from those events can be accurately5 measured by the unit of years. If, however, we attempt to ascertain the date of any event which happened outside the historical limit, we shall find that it is a question solely6 of relation. When we speak, for example, of the neolithic7 age, we merely mean a certain stage of human progress which succeeded the pal8?olithic,135 and preceded the bronze age, but we have no proof of the length of the interval dividing it from the one or the other. The historic “when?” implies “how long ago?” the prehistoric “when?” merely implies a definition before and after certain events, without any idea of the measurement of the intervals9.
An attempt to ascertain the absolute date of prehistoric events must of necessity fail, since it is based on the improbable assumption that the physical agents have acted uniformly, and that therefore the results may be used as a natural chronometer10. The present rate of the accumulation of débris, as at the Victoria Cave of the preceding chapter, or of that of silt11 in the deltas12 of rivers, such as the Nile, or the Tinière, may convey a rough idea of the high antiquity13 of prehistoric deposits; but a slight change either of the climate, or of the rainfall, would invalidate the conclusion. When the greater part of Europe lay buried under forest, when Palestine supported a large population, and when glaciers14 crowned some of the higher mountains of Africa, such as the Atlas15, the European and Egyptian climates were probably moister than at the present time, and the rainfall and the floods greater, and consequently the accumulation of sediment16 quicker than the observed rate under the present conditions. And in the same way all estimates of the lapse17 of past time, based upon the excavation18 of a river valley, or the retrocession of a waterfall, such as Niagara, lie open to the same kind of objection. It is not at all reasonable to suppose that the complex conditions which regulate the present rate of erosion, have been the same during the time the work has been done, and it therefore follows that the work done is a measure of the power employed, and not of136 the length of time during which it has been in operation. We must, therefore, give up the idea of measuring the past beyond the memory of man, as represented in historical documents, by the historic unit of years. We can merely trace a definite sequence of events, separated one from another by uncertain intervals. And for that series of events which extends from the borders of history back to the remote age where the geologist19, descending20 the stream of time, meets the arch?ologist, I have adopted the term prehistoric.85
The Prehistoric Fauna.
The prehistoric period is characterized by the arrival of the domestic animals in Europe, under the care of man. The dog, swine, horse, horned-sheep, goat, Bos longifrons, and the larger ox descended21 from an ancestor, according to Professor Rütimeyer, of the type of the great Urus, make their appearance together, in association with the remains22 of man, in the neolithic stage of civilization.86 Subsequently they spread over the whole of our continent, for the most part under the care of man. The Bos longifrons, however, and possibly also the Urus, reverted24 to feral conditions, just as the horses and oxen, in the Americas and Australia, have done at the present time, and their remains are therefore frequently found in association with animals undoubtedly25 wild. The domestic horse, the variety of hog26 descended from the wild boar, and the domestic cattle derived27 from the Urus, may possibly have passed under the yoke28 of man,137 in Europe, since their wild stocks were to be found in that area, both in the prehistoric and pleistocene times. This, however, cannot be affirmed of the swine descended from the southern variety of Sus Indica, or of the Celtic shorthorn, of the sheep, or goat, since their wild ancestors were not indigenous29 in Europe. These animals must have been domesticated30 in some area outside Europe; and since central Asia is the region where the wild stocks still exist, from which all the domestic animals are descended, it is reasonable to suppose that they were domesticated in that region, and thence introduced, by a race of shepherds and herdsmen, into our quarter of the world.
This conclusion is considerably31 strengthened by the evidence which Professor Heer has advanced, as to the vegetables used by the dwellers32 on piles in the Swiss lakes, among which some, such as the two kinds of millet33, the six-rowed barley34 (hordeum hexastichon), the Egyptian wheat (triticum turgidum), and a weed (Silene cretica), accidentally brought along with them, are distinctively36 of southern derivation.
The most important wild animals living in this country during the prehistoric period are the urus, the gigantic skulls37 of which occur in the peat bogs39 of England and Scotland, the Irish elk40, the moose (Cervus alces), and the reindeer41. The two last are far more abundant in the north than in the south of Britain; their remains have been discovered in the neighbourhood of London, those of both animals at Walthamstow, and those of the latter at Crossness in Kent, on the banks of the Thames. The remains of the bison have not been recorded from any prehistoric deposit in this country.
The Irish elk is the only animal which has become138 extinct; while the moose, or true elk, is the only wild species which has not been proved to have been living in the preceding age. The stag was very abundant.
The prehistoric fauna is distinguished42 from that of the pleistocene not merely by the appearance of the animals above mentioned, which were hitherto unknown, but by the absence of many species which were living during the latter period. The cave bear, woolly rhinoceros43, and mammoth44, for example, became extinct, the musk-sheep and lemming were banished45 from a temperate46 latitude47 to take refuge in the regions of the north, while the spotted48 hy?na, the hippopotamus49, and Felis caffer, retired50 to the warm regions of Africa, where they are still living.
The Arch?ological Classification.
The prehistoric period has been classified by the arch?ologists according to the stages of human progress which it presents. At the frontier of history, in each country, we find that the dwellers were acquainted with the use of iron, and had found it to be the most convenient material for the manufacture of cutting weapons and implements51. Before this the voice of tradition points out that bronze was the only material used for these purposes, and stone before bronze. These three stages of human culture, or the ages of iron, bronze, and stone, have been fully53 verified by investigations54 which have been made in various parts of Europe, into the prehistoric habitations and burial-places of man.
This classification by no means implies an exact chronology, or that any one of these ages, with the exception perhaps of the first, covered the whole of Europe at the same point of time, but that the order in139 which they followed each other is the same in each country which has been explored. There is good reason for the belief, that at the time the Egyptian and Assyrian empires were in the height of their glory, Northern Europe was inhabited by rude polished-stone-using races. And it is a well-ascertained fact, that while the inhabitants of Britain and Scandinavia were in their bronze age, the Etruscans and Ph?nicians were in their full power in the south. It is obvious again, that, even in the same country, the poorer classes must have been long content to use the ruder and more common materials for their daily needs, while the richer and more powerful used the rarer and more costly55. These three ages must therefore necessarily overlap56. “Like the three principal colours of the rainbow,” writes Mr. Evans,87 “these three stages of civilization overlap, intermingle, and shade off the one into the other; and yet their succession, as far as Western Europe is concerned, appears to be equally well defined with that of the prismatic colours, though the proportions of the spectrum57 may vary in different countries.” They cannot reasonably be viewed as hard and fast lines of division, mapping off successive quantities of time.
The age of stone is subdivided58 by Sir John Lubbock into the neolithic periods, or that in which polished stone was the only material used for cutting, and the pal?olithic, in which mankind had not learnt to grind and polish his implements. The latter belongs to the pleistocene, or quaternary period, since the pal?olithic implements are found in association with the remains of the animals characteristic of that age.
The prehistoric caves, therefore, may be divided into three classes if the arch?ological method of analysis be140 employed: 1, into those containing evidence of the use of iron; 2, those containing proof of the knowledge of bronze; 3, and lastly, those in which traces of polished stone weapons have been discovered unassociated with metals. By the animal remains which they contain they may be distinguished from those of the pleistocene age, both by the absence, as well as the presence of certain species which have been enumerated59.
From the arch?ological point of view, two out of the four ages are still represented. Stone is, at the present time, the only material used in the more remote regions of Australia, although it is fast being replaced by iron, which has superseded60 bronze, and is spreading rapidly over the whole earth. The group of historic caves described in the preceding chapter may be said to belong to the iron age, that is to say, to that later portion of it in which the events are recorded in history.
The traces of the occupation of caves by man in the iron and bronze ages are so extremely scarce, that it is certain that they were but rarely used as habitations. Man had sufficiently61 advanced in civilization in those times to construct artificial dwellings62 and tombs for himself, instead of using the natural shelters which were so very generally occupied in Europe by his ruder neolithic predecessors63.
Cave of the Iron Age.
In the course of the systematic64 exploration of caves in the Mendip Hills, carried on by Messrs. Ayshford Sanford, Parker, and myself, a cave was examined in Burrington Combe, near Wrington, in Somerset, which may be referred to the iron age, and which we named Whitcombe’s Hole. It opened upon the side of that141 magnificent combe, at a height of about 135 feet from the bottom and fifteen from the top, and ran horizontally inwards, the floor being formed of an accumulation of earth mingled65 with charcoal66, and containing numerous broken bones and teeth. The latter belonged to the wolf, fox, badger67, rabbit, hare, stag, goat, and Celtic shorthorn. In the lower portion were the fragments of a rude, unornamented urn69 of a coarse black ware70, with the rim71 turned at right angles, along with a bent72 piece of iron, which bears a strong resemblance to those found strengthening the corners of wooden coffins73 in the Gallo-Roman graves on the banks of the Somme. The fractures of the bones, with one exception, were caused by the hand of man, and not by the teeth of the carnivora. The position renders the cave eminently74 fitted for concealment75, for while commanding an extensive view down the Combe, it is invisible both from above and below, and opening on the face of an almost vertical76 cliff, it is easily defended. If the urn be sepulchral77, the interment must be of a later date than the occupation, because it is made in the débris which resulted from the latter.88
Caves of the Bronze Age in Britain.
The cave of Heathery Burn,89 near Stanhope, in Weardale, co. Durham, is the only one in this country that has furnished a large series of articles of the bronze age. It is described by Mr. Elliott as running into the142 precipitous side of a ravine, at a height of about 10 to 12 feet above the level of the Stanhope Burn, and as being partially78 traversed by water. Since its discovery in 1861, it has been altogether destroyed by the removal of the stone to be used as a flux79 in smelting80 the ore of the Weardale Iron Company, and an admirable section of its contents was therefore visible from time to time. A stratum81 of sand at the bottom, two feet nine inches thick, deposited by the stream, and containing angular masses of limestone82 that had dropped from the roof, was covered by a sheet of stalagmite three inches in thickness. On this rested a mass of bones and implements imbedded in silt or sand, and sealed over by a thickness of stalagmite of from two to eight inches.

Fig83. 32.—Bronze Knife, Heathery Burn (natural size).

Fig. 33.—Bronze Armlet, Heathery Burn.

Fig. 34.—Bronze Spearhead, Heathery Burn (? size).
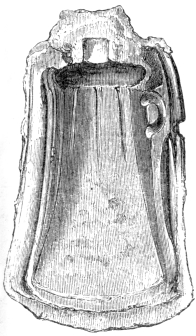
Fig. 35.—Bronze Mould for casting a socketed85 celt.
On removing the upper of these two stalagmitic floors a perfect human skull38 was discovered, along with broken bones of animals, charcoal, limpet shells, bone pins, an instrument of bone like a paper-knife, coarse pottery86 with fragments of chert imbedded in its mass, a portion of a jet armlet, as well as several boars’ tusks87. The same stratum at another place furnished a singular bronze knife with a socket84 for the handle (Fig. 32),90 bronze pins, celts, an armlet of twisted wire (Fig. 33), along with shells of limpet, mussel, and oyster88, and charcoal, and at a third, on the other side of the watercourse, a bronze143 spear-head. Subsequently, many articles were added to the above list, seven pins, three rings, two split-rings, a “razor,” disk, three socketed celts, one chisel89, two gouges90, and four spear-heads of bronze, and a fine bracelet91, and two ornaments92 of the horse-shoe, or split-ring type, made of thin plates of gold. One of the spear-heads, in the collection of the Rev23. Canon Greenwell, is represented in Fig. 34. There were also waste pieces of bronze, and the half of a bronze mould for casting celts, Fig. 35, in which one of the associated celts had actually been cast, since it is of the same pattern. These articles were probably concealed93 in the cavern94 by workers in bronze, who were prevented, by some unforeseen accident, from obtaining them again. The charcoal and the broken bones of the Bos longifrons, badger, and dog, imply that the cave had been used as a habitation; and possibly the two human skulls, which have been described by Professor Huxley and Mr. Carter Blake, may have belonged to the possessors of the hoard95 of bronze and gold. Both were discovered in the same stratum and below the floor of stalagmite.
The more perfect of the two skulls is considered by Professor Huxley to belong to the same long-headed race of men as that found at Muskham, in the valley of the Trent,—to a form which he terms the River-bed type, and that cannot be separated from those obtained from the long tumuli of the South of England, and considered by Dr. Thurnam to belong to a Neolithic Basque, or Iberian population.
Articles distinctly of the bronze age have been already noticed as having been met with in the caves of Kirkhead, in Cartmell, and in Thor’s Cave, in Staffordshire. From the latter the bracelet of thin bronze, Fig. 31, was145 obtained by Mr. Carrington, of Wetton. The rarity of bronze implements in caves in Britain and the Continent is probably, to a large extent, due to the value of the material, and to the fact that it could be re-melted. If a bronze article happened to be broken, the pieces would naturally be kept for future use, and not thrown away, as in the case of a fractured stone implement52. The former, therefore, are rare, the latter comparatively abundant.
The cave called the Cat-Hole, in Gower (Glamorgan), explored by Colonel Wood in 1864, contained several human skeletons, flint flakes97, fragments of red pottery marked with a string, cut bones, a stone muller, and a bronze socketed celt. The last is of the same pattern as some of those in the collection of the Rev. Canon Greenwell, from Heathery Burn, and has been cast in a mould similar in size and ornamentation to that figured in woodcut 35.
The Caves of Césareda probably occupied by Cannibals.
The contents of three caves91 in the Iberian peninsula, referable to the dawn of the bronze age, render it very probable that the use of human flesh was not unknown in those times.
In 1867 Senhor J. L. Delgado described his researches in the caverns98 of Césareda, in the valley of the Tagus, in the Casa da Maura, Lapa Furada, and Cova da Maura.146 The first of these contained two distinct strata99. The lower, consisting of sand mixed with fragments of rock, rested on the stalagmite, and contained fragments of charcoal, one implement of bone, and many of flint, a scraper, a flake96, and an arrow-head. The broken bones and teeth belonged to the following animals:—The lynx, fox, brown-bear, dog and wolf, a species of deer, the water-vole, and the rabbit. None of the remains of the carnivora had been subjected to the action of fire, or had been used for food. A human skull with lower jaw100 was dug out of the deepest part, but, since the matrix had been disturbed, it had probably been interred101 after the accumulation of the deposit.
It is recognized by Professor Busk92 as belonging to the same long type as the skulls of the caves of Gibraltar and the Basque graveyard102, measuring in length 6·7 inches, in breadth 5·3, in height 5·5, and therefore possessing cephalic and latitudinal103 indices of ·785 and ·820.93
The upper stratum, a sandy loam104, contained a large quantity of stones, and numerous articles fabricated by man: polished-stone axes, flakes, and other instruments of flint, bone, and antler, fragments of coarse black pottery, with bits of calcareous spar imbedded in its substance, and two plates of schist ornamented68 with a rude design, which may have been used as amulets106. Fragments of charcoal were scattered107 throughout the matrix, and adhered to some of the pottery and to the burnt pebbles108. The most abundant remains were those of man. They were to be counted by thousands, and were so fragmentary and scattered that it was impossible147 to put together one perfect skeleton. The teeth, belonging for the most part to children or fully-grown adults, were particularly abundant. The long bones had lost, very generally, their articular ends, had been fractured longitudinally, and some of them had been cut and scraped. It is therefore probable that this accumulation was formed by a tribe of cannibals: the evidence that human flesh formed their principal food being precisely109 of the same nature as that by which the flint-folk of the Périgord are proved to have subsisted110 on the flesh of the reindeer. Professor Busk,94 however, is inclined to believe the facts in support of cannibalism111 insufficient112. The associated animals consisted of the bat, dormouse, rabbit, horse, a small ox, allied113 to Bos longifrons, sheep or goat, wild cat, wolf, fox, and dog. The contents of the other two caves were precisely of the same nature, and had been accumulated under the same conditions.
A bronze arrow-head, discovered in the upper stratum, and the ornamentation of the stone amulet105, consisting of alternate triangles and zigzag114 ladders, as remarked by Mr. John Evans, indicate that the upper deposit belongs to the age of bronze, and probably to an early stage, when stone was being superseded by bronze, since many stone celts were found in the same spot.
The ancient burial-places of Ultz, in Westphalia, furnish a second case of the practice of cannibalism, according to M. Schaaffhausen of Bonn95. They are probably of the age of bronze.
148
The Cave of Reggio, in Modena.
The human remains in a cave in the province of Reggio,96 on the northern flank of the Apennines, brought before the Prehistoric Congress at Bologna by M. l’Abbé Chierici, and considered by him to be proofs of cannibalism, are probably merely the result of interment in a refuse-heap that had previously115 been accumulated. They were associated with bronze pins, rivets116, polished-stone axes, and various implements of bone, fragments of pottery and of charcoal, bones of pig, sheep, and dog, and belong therefore to the period of transition from the neolithic to the bronze age.
The caves have contributed but very little to our knowledge of the bronze-folk in any part of Europe. Examples, such as those given above, are scattered through France and Spain, but they are not sufficiently important to require notice. We could not expect that men, in the high state of civilization implied by the beautiful jewellery and ornaments which are distinctive35 of the bronze-folk, would have chosen the wild, half-savage life which is involved in cave-habitation.

点击 收听单词发音
收听单词发音
 收听单词发音
收听单词发音
1
prehistoric

|
|
| adj.(有记载的)历史以前的,史前的,古老的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
2
fauna

|
|
| n.(一个地区或时代的)所有动物,动物区系 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
3
ascertain

|
|
| vt.发现,确定,查明,弄清 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
4
interval

|
|
| n.间隔,间距;幕间休息,中场休息 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
5
accurately

|
|
| adv.准确地,精确地 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
6
solely

|
|
| adv.仅仅,唯一地 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
7
neolithic

|
|
| adj.新石器时代的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
8
pal

|
|
| n.朋友,伙伴,同志;vi.结为友 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
9
intervals

|
|
| n.[军事]间隔( interval的名词复数 );间隔时间;[数学]区间;(戏剧、电影或音乐会的)幕间休息 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
10
chronometer

|
|
| n.精密的计时器 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
11
silt

|
|
| n.淤泥,淤沙,粉砂层,泥沙层;vt.使淤塞;vi.被淤塞 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
12
deltas

|
|
| 希腊字母表中第四个字母( delta的名词复数 ); (河口的)三角洲 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
13
antiquity

|
|
| n.古老;高龄;古物,古迹 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
14
glaciers

|
|
| 冰河,冰川( glacier的名词复数 ) | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
15
atlas

|
|
| n.地图册,图表集 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
16
sediment

|
|
| n.沉淀,沉渣,沉积(物) | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
17
lapse

|
|
| n.过失,流逝,失效,抛弃信仰,间隔;vi.堕落,停止,失效,流逝;vt.使失效 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
18
excavation

|
|
| n.挖掘,发掘;被挖掘之地 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
19
geologist

|
|
| n.地质学家 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
20
descending

|
|
| n. 下行 adj. 下降的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
21
descended

|
|
| a.为...后裔的,出身于...的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
22
remains

|
|
| n.剩余物,残留物;遗体,遗迹 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
23
rev

|
|
| v.发动机旋转,加快速度 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
24
reverted

|
|
| 恢复( revert的过去式和过去分词 ); 重提; 回到…上; 归还 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
25
undoubtedly

|
|
| adv.确实地,无疑地 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
26
hog

|
|
| n.猪;馋嘴贪吃的人;vt.把…占为己有,独占 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
27
derived

|
|
| vi.起源;由来;衍生;导出v.得到( derive的过去式和过去分词 );(从…中)得到获得;源于;(从…中)提取 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
28
yoke

|
|
| n.轭;支配;v.给...上轭,连接,使成配偶 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
29
indigenous

|
|
| adj.土产的,土生土长的,本地的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
30
domesticated

|
|
| adj.喜欢家庭生活的;(指动物)被驯养了的v.驯化( domesticate的过去式和过去分词 ) | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
31
considerably

|
|
| adv.极大地;相当大地;在很大程度上 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
32
dwellers

|
|
| n.居民,居住者( dweller的名词复数 ) | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
33
millet

|
|
| n.小米,谷子 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
34
barley

|
|
| n.大麦,大麦粒 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
35
distinctive

|
|
| adj.特别的,有特色的,与众不同的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
36
distinctively

|
|
| adv.特殊地,区别地 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
37
skulls

|
|
| 颅骨( skull的名词复数 ); 脑袋; 脑子; 脑瓜 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
38
skull

|
|
| n.头骨;颅骨 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
39
bogs

|
|
| n.沼泽,泥塘( bog的名词复数 );厕所v.(使)陷入泥沼, (使)陷入困境( bog的第三人称单数 );妨碍,阻碍 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
40
elk

|
|
| n.麋鹿 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
41
reindeer

|
|
| n.驯鹿 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
42
distinguished

|
|
| adj.卓越的,杰出的,著名的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
43
rhinoceros

|
|
| n.犀牛 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
44
mammoth

|
|
| n.长毛象;adj.长毛象似的,巨大的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
45
banished

|
|
| v.放逐,驱逐( banish的过去式和过去分词 ) | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
46
temperate

|
|
| adj.温和的,温带的,自我克制的,不过分的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
47
latitude

|
|
| n.纬度,行动或言论的自由(范围),(pl.)地区 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
48
spotted

|
|
| adj.有斑点的,斑纹的,弄污了的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
49
hippopotamus

|
|
| n.河马 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
50
retired

|
|
| adj.隐退的,退休的,退役的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
51
implements

|
|
| n.工具( implement的名词复数 );家具;手段;[法律]履行(契约等)v.实现( implement的第三人称单数 );执行;贯彻;使生效 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
52
implement

|
|
| n.(pl.)工具,器具;vt.实行,实施,执行 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
53
fully

|
|
| adv.完全地,全部地,彻底地;充分地 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
54
investigations

|
|
| (正式的)调查( investigation的名词复数 ); 侦查; 科学研究; 学术研究 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
55
costly

|
|
| adj.昂贵的,价值高的,豪华的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
56
overlap

|
|
| v.重叠,与…交叠;n.重叠 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
57
spectrum

|
|
| n.谱,光谱,频谱;范围,幅度,系列 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
58
subdivided

|
|
| 再分,细分( subdivide的过去式和过去分词 ) | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
59
enumerated

|
|
| v.列举,枚举,数( enumerate的过去式和过去分词 ) | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
60
superseded

|
|
| [医]被代替的,废弃的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
61
sufficiently

|
|
| adv.足够地,充分地 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
62
dwellings

|
|
| n.住处,处所( dwelling的名词复数 ) | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
63
predecessors

|
|
| n.前任( predecessor的名词复数 );前辈;(被取代的)原有事物;前身 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
64
systematic

|
|
| adj.有系统的,有计划的,有方法的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
65
mingled

|
|
| 混合,混入( mingle的过去式和过去分词 ); 混进,与…交往[联系] | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
66
charcoal

|
|
| n.炭,木炭,生物炭 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
67
badger

|
|
| v.一再烦扰,一再要求,纠缠 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
68
ornamented

|
|
| adj.花式字体的v.装饰,点缀,美化( ornament的过去式和过去分词 ) | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
69
urn

|
|
| n.(有座脚的)瓮;坟墓;骨灰瓮 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
70
ware

|
|
| n.(常用复数)商品,货物 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
71
rim

|
|
| n.(圆物的)边,轮缘;边界 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
72
bent

|
|
| n.爱好,癖好;adj.弯的;决心的,一心的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
73
coffins

|
|
| n.棺材( coffin的名词复数 );使某人早亡[死,完蛋,垮台等]之物 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
74
eminently

|
|
| adv.突出地;显著地;不寻常地 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
75
concealment

|
|
| n.隐藏, 掩盖,隐瞒 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
76
vertical

|
|
| adj.垂直的,顶点的,纵向的;n.垂直物,垂直的位置 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
77
sepulchral

|
|
| adj.坟墓的,阴深的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
78
partially

|
|
| adv.部分地,从某些方面讲 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
79
flux

|
|
| n.流动;不断的改变 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
80
smelting

|
|
| n.熔炼v.熔炼,提炼(矿石)( smelt的现在分词 ) | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
81
stratum

|
|
| n.地层,社会阶层 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
82
limestone

|
|
| n.石灰石 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
83
fig

|
|
| n.无花果(树) | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
84
socket

|
|
| n.窝,穴,孔,插座,插口 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
85
socketed

|
|
| v.把…装入托座(或插座),给…装上托座(或插座)( socket的过去分词 );[高尔夫球]用棒头承口部位击(球) | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
86
pottery

|
|
| n.陶器,陶器场 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
87
tusks

|
|
| n.(象等动物的)长牙( tusk的名词复数 );獠牙;尖形物;尖头 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
88
oyster

|
|
| n.牡蛎;沉默寡言的人 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
89
chisel

|
|
| n.凿子;v.用凿子刻,雕,凿 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
90
gouges

|
|
| n.凿( gouge的名词复数 );乱要价;(在…中)抠出…;挖出…v.凿( gouge的第三人称单数 );乱要价;(在…中)抠出…;挖出… | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
91
bracelet

|
|
| n.手镯,臂镯 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
92
ornaments

|
|
| n.装饰( ornament的名词复数 );点缀;装饰品;首饰v.装饰,点缀,美化( ornament的第三人称单数 ) | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
93
concealed

|
|
| a.隐藏的,隐蔽的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
94
cavern

|
|
| n.洞穴,大山洞 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
95
hoard

|
|
| n./v.窖藏,贮存,囤积 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
96
flake

|
|
| v.使成薄片;雪片般落下;n.薄片 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
97
flakes

|
|
| 小薄片( flake的名词复数 ); (尤指)碎片; 雪花; 古怪的人 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
98
caverns

|
|
| 大山洞,大洞穴( cavern的名词复数 ) | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
99
strata

|
|
| n.地层(复数);社会阶层 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
100
jaw

|
|
| n.颚,颌,说教,流言蜚语;v.喋喋不休,教训 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
101
interred

|
|
| v.埋,葬( inter的过去式和过去分词 ) | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
102
graveyard

|
|
| n.坟场 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
103
latitudinal

|
|
| adj.纬度的,纬度方向的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
104
loam

|
|
| n.沃土 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
105
amulet

|
|
| n.护身符 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
106
amulets

|
|
| n.护身符( amulet的名词复数 ) | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
107
scattered

|
|
| adj.分散的,稀疏的;散步的;疏疏落落的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
108
pebbles

|
|
| [复数]鹅卵石; 沙砾; 卵石,小圆石( pebble的名词复数 ) | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
109
precisely

|
|
| adv.恰好,正好,精确地,细致地 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
110
subsisted

|
|
| v.(靠很少的钱或食物)维持生活,生存下去( subsist的过去式和过去分词 ) | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
111
cannibalism

|
|
| n.同类相食;吃人肉 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
112
insufficient

|
|
| adj.(for,of)不足的,不够的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
113
allied

|
|
| adj.协约国的;同盟国的 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
114
zigzag

|
|
| n.曲折,之字形;adj.曲折的,锯齿形的;adv.曲折地,成锯齿形地;vt.使曲折;vi.曲折前行 | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
115
previously

|
|
| adv.以前,先前(地) | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
116
rivets

|
|
| 铆钉( rivet的名词复数 ) | |
参考例句: |
|
|
|
| 欢迎访问英文小说网 |

